IBM & Red Hat on AWS
Secure Resources in a Hybrid Environment Using IBM Verify and AWS IAM Identity Center
As organizations adopt cloud services, many are migrating, modernizing, and building new applications on AWS. These workloads often span multiple AWS services, like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) for compute, Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) for storage, Amazon Aurora for databases, and Amazon API Gateway for application integrations.
When using AWS services, organizations need to manage access to AWS resources securely, efficiently, and at scale. This requires identity integration across the enterprise. IBM Verify Identity Fabric helps customers integrate and manage identity across their cloud and on-premises resources.
In this blog post, you will learn how IBM Verify with AWS IAM Identity Center can be used to create an identity solution designed for security and scalability in hybrid environments.
What is IBM Verify Identity Fabric?
Enterprises working with both cloud and on-premises environments can benefit from an integrated identity ecosystem to manage user authentication and control access. Identity Fabric is an approach that helps with identity and access management by integrating identity providers, authentication methods, and policy enforcement mechanisms. Using IBM Security Verify Identity Fabric, organizations can work toward a consistent identity framework across their hybrid environments.
With IBM Verify Identity Fabric, businesses can create secure user journeys across diverse environments while maintaining strong governance and threat detection. The following architecture diagram (Figure 1) illustrates this approach:
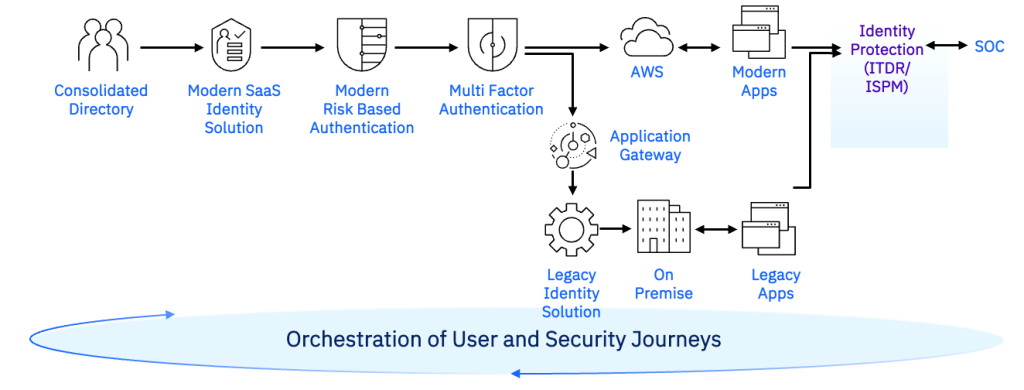
Figure 1. IBM Verify Identity Fabric orchestrates identity authentication workflows spanning AWS services and on-premises resources.
Components for successfully orchestrating security at scale
Consolidating Identity Silos
As shown in Figure 1, the workflow begins with a Consolidated Directory, which serves as a unified source for identities across the enterprise. This consolidated view feeds into the IBM Verify solution, which helps with centralized identity provisioning, lifecycle management, and policy enforcement. This forms the foundation for the identity fabric.
Enabling Risk-Based Authentication
The identity fabric uses a Risk-Based Authentication engine. This system evaluates contextual factors – such as device health, geolocation, and login behaviour – to help determine access risk. Combined with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), it can adjust access decisions based on detected risk levels. This approach authenticates users based on risk factors, rather than relying solely on static credentials.
Integrating Across Cloud and on-premises Applications
Users frequently need to access applications in both cloud and on-premises environments. As shown in Figure 1, the identity solution can help modern applications integrate through connectors, while legacy applications continue to operate through an Application Gateway and Legacy Identity Solution. This approach allows for incremental modernization without disrupting existing business processes.
Governing Privileged and Standard Identities
Identity governance helps address both user compliance and privileged access management. The identity fabric provides visibility into access permissions, justifications, and usage. This information can help implement least privilege principles and manage access permissions.
Delivering Actionable Insights with Identity Protection
A key component of this architecture is its capability to detect and respond to identity-based threats. Identity Threat Detection & Response (ITDR) and Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) together form the Identity Protection layer. This provides visibility into potentially suspicious activity, configuration changes, policy violations, and security gaps. Integration with a Security Operations Center (SOC) can help drive incident response and remediation. This approach allows organizations to incorporate threat awareness into identity security.
Solution Overview
By integrating IBM Security Verify with AWS IAM Identity Center, organizations can combine the authentication, governance, and lifecycle management capabilities of IBM Verify with the permission controls of AWS IAM Identity Center. This integration helps manage access to AWS services for today’s workforce needs.
The following architecture diagram (Figure 2) shows how IBM Security Verify integrates with AWS IAM Identity Center to help manage identity across hybrid environments:
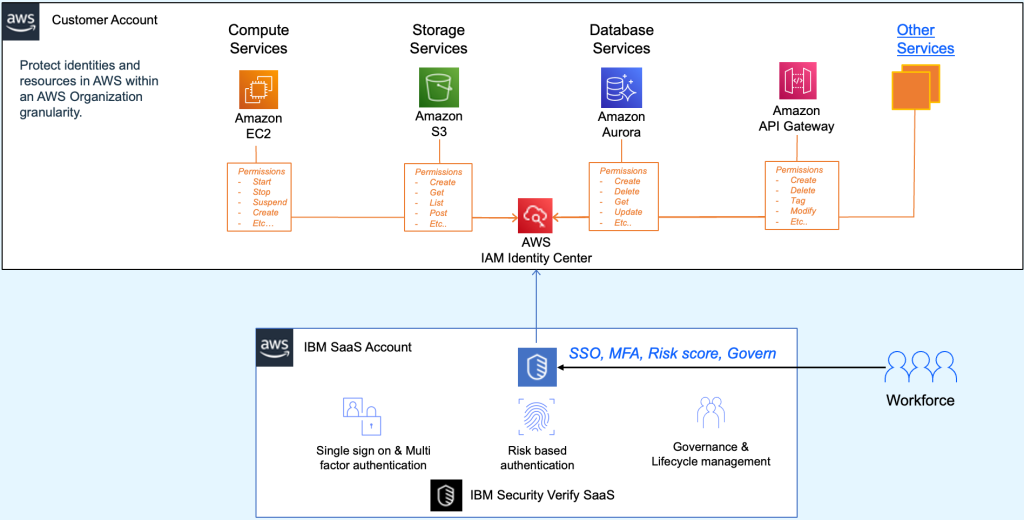
Figure 2. Integrating IBM Security Verify with AWS IAM Identity Center.
The key components of this architecture as shown in Figure 2 are below:
- IBM Security Verify SaaS provides identity management using the following features:
- Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Risk-based authentication to detect anomalies in real time
- Lifecycle management through SCIM provisioning
- AWS IAM Identity Center manages user access across AWS services such as:
- Amazon EC2 for compute
- Amazon S3 for storage
- Amazon Aurora for database services
- Amazon API Gateway integration services
Together, these components help safeguard identities, manage access to AWS resources, and automate user lifecycle tasks across the AWS environment.
Integration between AWS IAM Identity Center and IBM Verify SaaS
The integration between AWS IAM Identity Center and IBM Verify SaaS offers a hybrid identity model, combining AWS access management with enterprise IAM capabilities.
The key features of this integration include:
- Federated Identity Provider: IBM Verify functions as an external IdP to AWS Identity Center via OIDC or SAML.
- Advanced Authentication: AWS users can authenticate through IBM Verify using MFA, passkeys, or adaptive access policies.
- Lifecycle Orchestration: User provisioning and deprovisioning across AWS and non-AWS applications via SCIM connectors and workflows.
- Risk-Based Access: Help improve AWS access security using IBM’s risk scoring, behavioural analytics, and geo-aware policies.
- Hybrid Directory Synchronization: IBM Identity Bridge synchronizes users from on-premises directory services like Active Directory or LDAP to IBM Verify, and then to AWS Identity Center.
This integration is designed to help provide centralized identity control and improved user experience across AWS and non-AWS resources.
Legacy Integration and Hybrid Identity
IBM Verify SaaS on AWS works with systems and applications in both cloud and on-premises environments. The components of this integration are shown in Figure 3.
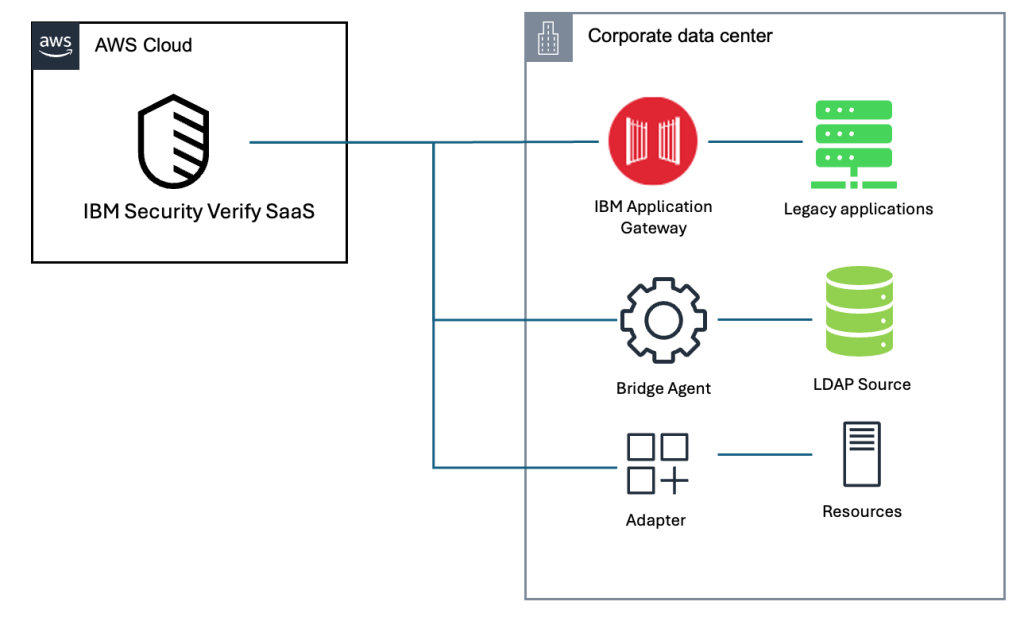
Figure 3. Integrating IBM Security Verify SaaS with on-premise environment.
As shown in Figure 3, the integration includes three main components. IBM Application Gateway helps provide SSO for legacy web applications using protocols like Kerberos or LTPA. Identity Bridge connects on-premises identity stores (AD, LDAP) with cloud services. The Adapter library helps secure enterprise applications including mainframes, databases, and HR systems. Together, these components help provide a unified identity experience across traditional, cloud, and SaaS applications.
Modular and Composable Deployment
IBM Verify SaaS on AWS supports modular implementation, working with the AWS approach to composable services:
- Customers can implement specific modules based on their requirements, including Multi-factor Authentication (MFA), Lifecycle Management, and Access Control.
- Organizations can add capabilities to AWS IAM Identity Center as their needs change, while maintaining their existing configuration. This helps minimize disruption to operations while adding functionality.
- Customers can scale their operations using a pay-as-you-grow licensing model.
This flexibility can help businesses with phased cloud migrations and extending their existing IAM implementations.
The benefits of IBM Verify SaaS on AWS include:
- Designed for scalability on AWS with availability features. IBM manages the infrastructure to help customers focus on building applications.
- Identity controls aligned with zero trust principles, including risk-based access and contextual policies that apply verification to requests.
- Integration with AWS services like AWS IAM Identity Center, Amazon CloudWatch and Amazon GuardDuty. This helps with user management, monitoring, and evaluating risk to protect mission critical applications.
- Integration patterns including:
- SAML-Based SSO Integration where IBM Security Verify acts as a SAML IdP for AWS user authentication. This integration works with multi-factor authentication (MFA) and adaptive access controls and helps provide access to AWS resources without requiring AWS credentials.
- SCIM-Based user provisioning that helps automate user provisioning and deprovisioning and assists with access governance. It also helps synchronize users and groups from IBM Verify to AWS IAM Identity Center.
Conclusion
The integration of IBM Verify SaaS with AWS IAM Identity Center is designed to help manage access to AWS services while maintaining user experience and operational visibility. By using IBM Security Verify with AWS IAM Identity Center, organizations can implement security controls and reduce manual tasks. This integrated solution can help organizations work toward providing appropriate access to IT resources based on user roles and requirements.
Get started by scheduling a free IBM Verify SaaS demo.
Additional Content
- Simplify security administration with AWS IAM Identity Center
- Build your identity workflow with AWS IAM Identity Center and external IdPs
- Implementing a Zero Trust security model with AWS services
- Learn more about AWS IAM Identity Center
- IBM Security Verify – AWS IAM Identity Center Configuration
- AWS IAM Identity Center – External IdP Setup Guide
- AWS IAM Identity Center SSO Documentation
Visit the AWS Marketplace and get started with IBM Security Verify offers on AWS
- AWS Marketplace: IBM Verify SaaS
- AWS Marketplace: IBM Security Verify Governance
- AWS Marketplace: IBM Security Verify Directory
- AWS Marketplace: IBM Verify Identity Access