Migration & Modernization
Moody’s Transforms CreditLens™ Change Management Platform with Innovative Serverless Architecture
This post is co-written with Vihang Shah from Moody’s.
Introduction
Managing change requests across hundreds of applications while maintaining operational excellence presents a complex challenge for growing SaaS companies. Manual processes that once worked for dozens of deployments become unsustainable bottlenecks when scaled to enterprise levels. A solution to these bottlenecks is serverless automation that will transform operational efficiency by orders of magnitude. Moody’s discovered this firsthand when they revolutionized their CreditLens change management process. This change management process is used to request changes to the CreditLens websites. By replacing manual workflows with intelligent serverless automation across over 750 websites, they achieved transformational results: an 83% reduction in change ticket turnaround time and saving 180 hours of manual operational efforts each month. These aren’t incremental improvements, they represent a fundamental shift in how change management operates at scale. Serverless technologies offload infrastructure management, freeing development teams to focus on innovation and delivering business value. These technologies also benefit operations teams by reducing the overhead of maintaining and scaling application infrastructure, allowing operations teams to focus on strategic initiatives and operational excellence.
The Moody’s team designed a solution using a combination of AWS Serverless services integrated with Jira and Jenkins pipelines. This post describes the key technical innovations implemented, including reliable event and message processing, automated parameter validation, enhanced pre-checks, and multi-region deployment capabilities.
The solution provides advanced change scheduling, Jenkins pipeline stability, and detailed tracing capabilities that improve enterprise-scale automation. Business impact extends far beyond efficiency gains, transforming how teams collaborate and deliver value. This post shares implementation insights and lessons learned, offering a practical guide for organizations pursuing similar transformations.
About Moody’s
Moody’s provides financial intelligence and analytical tools to help financial institutions make better, faster decisions. With a history rooted in Moody’s century-long legacy of credit ratings and risk expertise, Moody’s helps banks, insurers, asset managers, and corporations with solutions for credit analysis, economic research, regulatory compliance, and financial modeling.
About CreditLens
Moody’s developed and launched the CreditLens solution in 2017 to digitize and modernize the credit origination process, empowering financial institutions to achieve greater efficiency and consistency in credit decisioning. The platform integrates data, analytics, and workflow automation to streamline credit assessment and enhance risk management. Today, the solution is a foundational component of the Moody’s Lending Suite, a comprehensive end-to-end solution that supports the full loan lifecycle—from origination and underwriting to loan portfolio monitoring and management.
The business challenge
Under the legacy change control process, the change requestors follow an internal process to request an operation on the applications. This involves creating a manual change request through Jira and submitting it for review. The change ticket will then go through a review process to ensure the intended operation is viable. When the case needs additional information, the process might take longer to ensure accuracy.
After approving the change ticket, an operations team member will implement the change in the maintenance window or at the requested time. During release cycles, the workload increases, requiring close coordination between operations managers and the team implementing the changes to ensure the servicing of all approved change requests.
The team focused on three key areas: addressing urgent client requests, managing staff availability during weekends or holidays, and maintaining clear communication with change requestors. These factors presented an opportunity to implement a streamlined, automated approach to implement change tickets for key business workflows that enhance the end-user experience along with improving operation efficiency and security.
Solution Overview and Design
Moody’s strategically transitioned to an automated change implementation process following the review and approval of the change ticket from its change committee. The DevOps team leveraged managed services such as AWS Lambda, Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS), Amazon EventBridge Pipes, Amazon API Gateway, and AWS Step Functions to design the solution. This lets the DevOps team concentrate on automating core business logic while reducing operational overhead for both the engineering and operations teams. The following diagram illustrates the solution architecture.
Solution Architecture
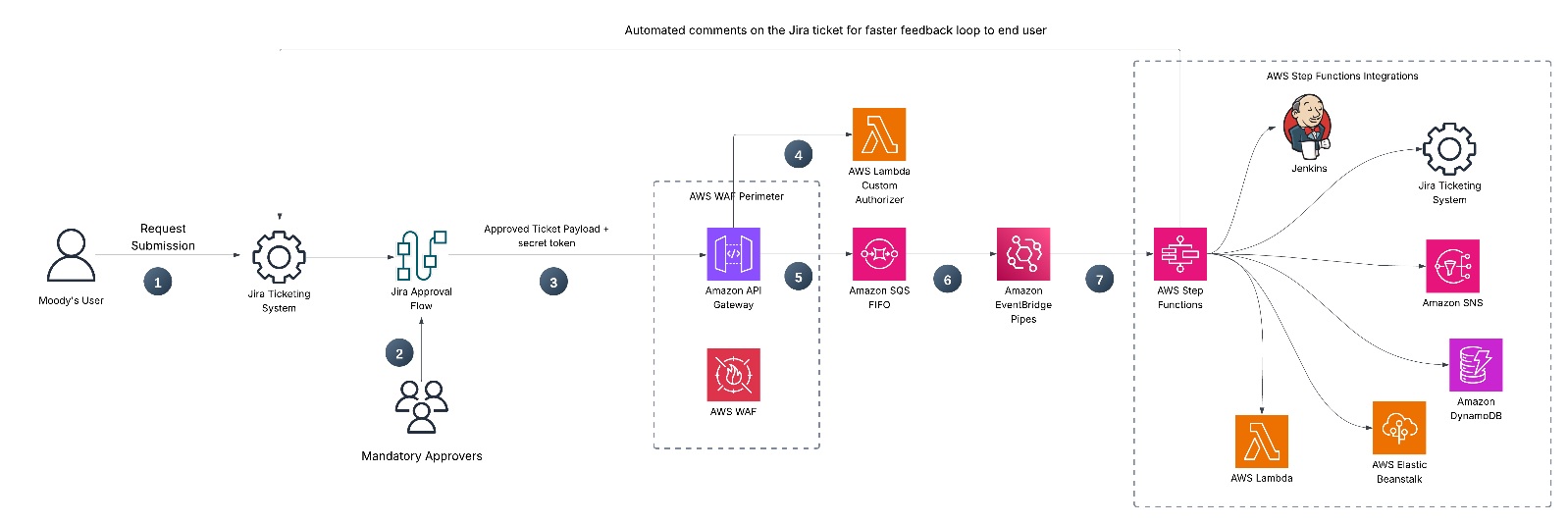
Figure 1: Solution Architecture
The design flow comprises the following steps:
- Change requestors (client services teams, project managers, and internal users) submit their requests through a pre-defined form on an internal Jira portal. The requestor must provide details such as the application URL, the type of operation intended along with additional required details, and the desired timing for the change.
- The request converts into a change ticket, with the required fields completed and assigned to mandatory reviewers from the change committee for approval.
- Once approved, a webhook in Jira sends the ticket payload and a secret token to API Gateway.
- API Gateway invokes a Lambda authorizer to validate and authorize the request.
- After authorization, API Gateway sends the payload data to an Amazon SQS FIFO queue, preserving its priority.
- Amazon SQS FIFO integrates with Amazon EventBridge Pipes, providing direct, point-to-point integration with no custom Lambda code in between.
- The EventBridge pipe invokes an AWS Step Function workflow with the SQS message payload, and the workflow performs pre-checks to confirm the ticket meets service requirements. It then uses a Wait state to schedule the change at the requested time, allowing change scheduling up to 14 days in advance.
- At the requested change time, the Step Function workflow proceeds with running the respective Jenkins pipeline with appropriate parameters, monitoring the build while leveraging the necessary error handling mechanisms.
- AWS Step Functions evaluates the Jenkins execution status and automatically executes the appropriate response workflow. Successful deployments complete the change request and notify the change requestor. A failure triggers an automated incident management process that creates a child ticket in Jira and notifies the Cloud Operations team for resolution.
Security Guardrails
The solution implements the following security measures:
- Third Party Ticketing Controls. The ticketing system integrates with the existing single sign-on solutions and requires multi-factor authentication, ensuring that only authorized internal users submit change requests through the Jira portal.
- Amazon API Gateway. AWS Web Application Firewall (AWS WAF) protects API Gateway. It restricts access to requests solely from Jira IP ranges. In addition, the Cloud Operations team manages custom rule groups and AWS Managed Rules, which offer protection against application vulnerabilities and unwanted traffic.
- AWS Step Function Permissions. The services integrated within AWS Step Functions, such as AWS Lambda, use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles that follow the Principle of Least Privilege. This ensures the service has only the necessary permissions to interact with required services and maintains read-only IAM access to application environments like AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
Multi-Region and Multi-Account Deployment Strategy
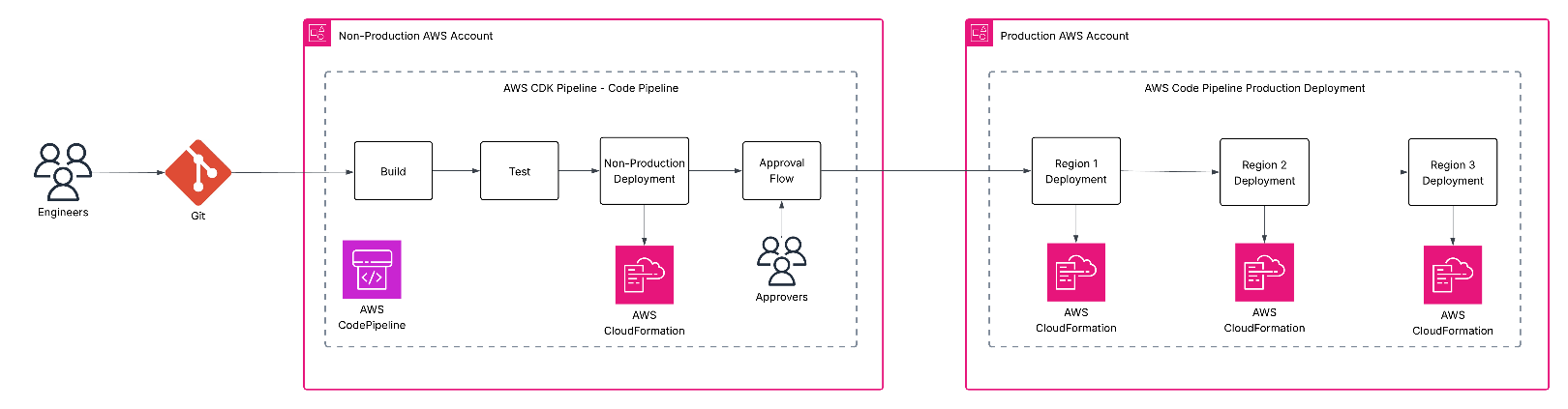
Figure 2 : Multi-Region and Multi-Account Deployment
The deployment strategy leverages AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) Pipelines, which streamlines the deployment of one or more instances of the CDK applications using AWS CloudFormation. By handling the complexities of cross-account pipeline setup, CDK Pipelines lets the teams focus on implementing the required business logic for successful pipeline creation.
DevOps engineers commit code to the Git repository and merge the changes into the main branch after receiving the required approvals. Once merged, an AWS CodePipeline pipeline is invoked to build and test the CDK applications before deploying them to the non-production account.
Following deployment to a non-production environment, the team validates the CDK application functionality regarding the requirements. An approval gate ensures every stakeholder reviews and approves the change. Once approved, the pipeline deploys the CDK application to the production account across the required production regions using AWS CloudFormation.
Key business outcomes and process benefits
Process efficiency results
- The team realized an 83% reduction in change implementation turnaround time across more than 750 CreditLens websites. This significantly shortens the interval from change request submission to approval and implementation. This substantially improves process efficiency for the Cloud Operations teams.
- At the time of this writing, this process has saved the Cloud operations team an average of 180 hours per month since its production launch, letting them dedicate more time towards strategic initiatives that drive the organization forward.
Streamlined Workflow Automation and Change Scheduling
Integrating a change management platform with a serverless workflow enables automatic execution of deployment and operational tasks. Project managers and internal users schedule changes in advance (including weekends and holidays) or request immediate change implementation for certain types of changes after approval. Users simply fill out a request form, and once approved, the workflow automates the change implementation, providing regular status updates through comments on the change ticket. If an error occurs, the workflow creates child tickets automatically and sends a notification to the operations team.
Multi-Region Support
The serverless workflow is deployable across multiple AWS regions and delivers consistent operation in every location. Change requestors are not required to specify the website’s region, as the workflow automatically identifies and executes changes in the appropriate region based on the provided information.
Enhanced Security
End-to-end integration between the change management platform and deployment pipelines means end-users don’t need access to infrastructure or deployment tools. This lets operations teams restrict access to the environment, improving overall security. In addition, monitoring tools like AWS X-Ray integrate into the workflow for detailed visibility and tracing capabilities for each change ticket implementation.
Robust Error Handling and Escape Hatch
The workflow includes automatic retries and exponential backoff for error handling, as well as message queuing to prevent data loss. Operations teams intervene and take control of the processes as needed, ensuring flexibility and reliability.
Improved Jenkins Pipeline Stability
By automating parameter checks through an AWS Step Functions workflow, the serverless workflow improves the stability of Jenkins pipelines. Change requestors don’t need training on any internal processes except for filling out a form, saving time for both technical and non-technical teams.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
- Leveraging Serverless Managed Services and Direct Integrations
- One key lesson learned was the efficiency gained by utilizing AWS serverless managed services. Establishing point-to-point integrations, such as connecting Amazon SQS directly to AWS Step Functions or EventBridge Pipes, minimizes the need to write custom AWS Lambda code. This approach reduced the operational overhead and maintenance burden associated with managing Lambda functions. It also improved reliability and performance by reducing custom logic and potential points of failure.
- Simplifying Multi-Account and Multi-Region Deployments with CDK Pipelines
- Another important takeaway was the value of AWS CDK Pipelines in streamlining the deployment process across multiple AWS accounts and regions. CDK Pipelines abstract away much of the complexity involved in configuring granular permissions, cross-account roles, and region-specific resources. This releases teams to focus on application logic and business requirements, rather than spending time on an intricate pipeline setup. By adopting CDK Pipelines, organizations accelerate their DevOps practices, ensure consistency, and reduce the risk of misconfiguration in complex, multi-environment deployments.
- Adopting Native Error Handling in AWS Step Functions
- A best practice that emerged from this experience was to fully utilize the native error handling capabilities in AWS Step Functions. By defining error-catching logic, retries, and fallback states directly within the workflow definition, teams gracefully handle task failures, transient issues, and unexpected errors. This approach not only improves the resilience and reliability of workflows but also simplifies troubleshooting and recovery. Leveraging these built-in features ensures workflows are robust and can automatically respond to failures without manual intervention, as detailed in the
AWS Step Functions error handling documentation
-
- .
Conclusion
This AWS serverless implementation has transformed CreditLens’s change management processes, delivering significant improvements in efficiency and operational agility. By automating manual workflows and integrating robust security and error-handling mechanisms, Moody’s reduced turnaround times and enabled smooth change implementations across multiple production regions. This solution empowers both technical and non-technical users to request and implement changes confidently while maintaining robust governance and security controls by the operations teams.
Where to Start
- Evaluate your current change management workflows to identify manual processes that could benefit from serverless automation, potentially reducing turnaround time.
- Calculate the operational hours currently spent on manual change management processes to quantify potential time savings.
- Review your current change implementation turnaround times and set targets for improvement through automation.
- Assess how automated change scheduling could improve service delivery during weekends and holidays without increasing staff workload.
References
Credit Risk Solutions & Management – Moody’s
Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) Documentation
Amazon EventBridge Pipes Documentation
Amazon API Gateway Documentation
AWS Step Functions Documentation
Visualize Lambda function invocations using AWS X-Ray – AWS Lambda