AWS Messaging Blog
Streamlining outbound emails with Amazon SES Mail Manager
In today’s digital landscape, efficient email management is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES) has long been a go-to solution for handling transactional and marketing emails. Through Mail Manager, Amazon SES offers powerful tools to enhance your email infrastructure, particularly for outbound email handling and archiving.
In this post, we explore how Mail Manager can modernize your approach to outbound email management. We’ll dive into the various options available for controlling email flows and archiving all outgoing emails. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of how you can use Mail Manager to:
- Strengthen your email infrastructure
- Simplify outbound email workflow management
- Help meet compliance through robust email archiving
In this post, we consider a real-world customer use case from a university where students should receive clean emails free from malware and phishing attempts. Amazon SES Mail Manager provides a comprehensive email pipeline that handles security screening, message archival, and reliable delivery. By implementing this system, the university significantly improved its email infrastructure, helping to ensure that important communications reach students safely and efficiently.
Walkthrough
In this walkthrough, we guide you through the process of configuring Amazon SES Mail Manager with the following components:
- Traffic policy: You’ll create a traffic policy designed to help ensure that students receive only clean, secure emails. The default action is set to
Deny all, providing a strict baseline. The policy includes two key statements connected by anORcondition. Policy Statement 1 allows emails if the recipient address is in theValid-Addresslist. Policy Statement 2 allows emails that meet all of the following conditions: not listed in Abusix Guardian Mail, recipient address is not in theInvalid-Email-List, and uses TLS protocol version 1.3 or higher. This configuration effectively filters potential threats while allowing legitimate communications to reach students’ inboxes, maintaining a secure email environment for the university. - Rule set: You’ll create a rule set containing two rules that execute in sequential order:
- Rule 1: Scan and isolate malicious content: Scans messages and, if the scan fails, stores emails in an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket for further validation and halts sending email.
- Rule 2: Archive and send clean emails to recipients: Archives all outgoing emails for audit and compliance after passing the security scan and routes emails to recipients.
- Ingress endpoint: You’ll create a Mail Manager ingress endpoint that will receive, route, and manage emails based on your configured policies and rules.
After setting up these components, you’ll use sample Python code to send an email through the ingress endpoint. To verify functionality, we’ll check the email archive to confirm that all incoming emails are archived for compliance or audit purposes and confirm email is received in the intended inbox. The workflow is shown in the following figure.
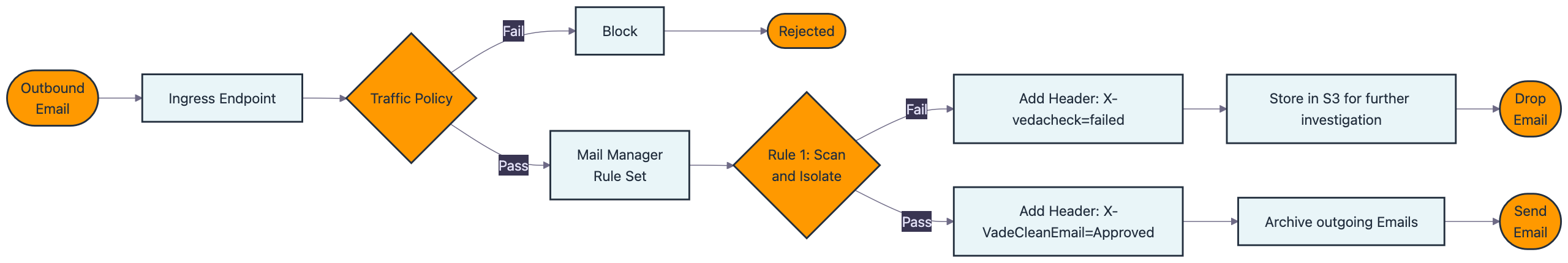
Prerequisites
Before beginning, make sure that you have completed domain verification in your desired AWS Region and moved out of the Amazon SES sandbox. Domain verification is a crucial first step that validates your authority to send emails through SES from your domain. In this tutorial, you’ll use a sample Python program to send emails programmatically through an ingress SMTP endpoint. You can run this program either on your local machine or using AWS CloudShell.
You should have:
- An active AWS account.
- Amazon SES
- AWS Secrets Manager
- AWS CloudShell
- A user signed in to the AWS Management Console must have permissions to the preceding above services.
Before creating traffic policies and rule sets, you will first set up Email Add Ons, and email archiving, and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles, which will be needed while creating traffic policies and rules.
Step 1: Enable Email Add Ons for Amazon SES Mail Manager
To implement security features such as malicious content scanning in your email workflow, first enable the necessary Email Add Ons:
- Open the AWS Management Console for Amazon SES.
- Choose Mail Manager and then Email Add Ons.
- Select your desired Add Ons:
- Trend Micro Virus Scanning
- Abusix Guardian Mail
- Spamhaus Domain Block List (DBL)
- Vade Advanced Email Security
- Choose Enable.
Important Notes:
- Email Add Ons are third-party security products integrated with Mail Manager
- Once subscribed, you can use them in your traffic policies or rule sets
As part of this post, you will be using the Abusix Guardian Mail and Vade Advanced Email Security Add Ons to enhance email security posture. It doesn’t mean you have to use all of them—you can subscribe to the ones that best fit your requirements based on your use case.


Step 2: Configure an email archive for compliance and retention
You will create an email archive to store outgoing messages to use as part of configuring Rule 2. This archive will serve as a repository for outgoing messages.
- Navigate to Mail Manager and then to Email Archiving.
- Choose Create archive.
- Complete the archive configuration:
- Enter a unique name in the Archive name field.
- (Optional) Select a retention period to override the default of 180 days.
- (Optional) Set up encryption by either entering your own AWS Key Management System (AWS KMS) key in the KMS key ARN field or selecting Create new key.
- Choose Create archive.
- After being created, this archive will store your emails according to the rules you’ll define in the next step.
Step 3: Create and S3 bucket and IAM role for S3 access
When emails fail the Vade security scan, they need to be stored securely for further investigation. In this step, we’ll create an S3 bucket to store these flagged emails and set up the necessary IAM permissions.
- Create an S3 bucket to quarantine suspicious and malicious emails identified by the Vade scanner. This bucket will store these emails for further investigation by the security team. Note the bucket name, because you’ll need it in the next step.
- Create an IAM role that allows Mail Manager to upload suspicious emails to an S3 bucket. This IAM role will be used in Rule 1 when configuring the Write to S3 rule action for storing emails that fail the security scan.
- Go to the IAM console.
- Choose Roles and then choose Create role.
- For trusted entity, select Custom trust policy and paste the following (replace
"XXXXXXXXXXX"with your AWS account ID). - Choose Next and create an inline policy with the following permissions (replace
"MyDestinationBucketName"with your S3 bucket name). - Enter a name your role and choose Create role.
Step 4: Create and IAM role permission policy for send to internet rule action
Configure an IAM role that permits Mail Manager to send emails to external domains. This role will be referenced in Rule 2 for delivering validated emails to recipients.
- You can either:
- Use the same IAM role created in Step 3 and add this policy, or
- Create a new IAM role and add the following permission policy (Replace
example.comwith your verified domain,"XXXXXXXXXXX"with your AWS account ID andmy-configuration-setwith your configuration set name if applicable).
This policy grants the necessary permissions to send emails to recipients on the internet, which will be used in rule 2 of your rule set.
- If adding to an existing role:
- Go to the IAM console and select your role
- Choose Add permissions and then select Create inline policy.
- Paste the preceding JSON and choose Review policy.
- Enter a name for the policy and choose Create policy.
- If you create a new role, name it appropriately and choose Create role.
Step 5: Create a traffic policy
Traffic policies serve as security checkpoints for your email infrastructure, controlling which messages can enter your system based on defined security rules. To create a traffic policy that enforces security requirements for your emails:
- Open the Amazon SES console.
- Go to Mail Manager and choose Traffic policies.
- Choose Create traffic policy.
- Enter a unique name for your policy.
- Set Default action to Allow (this handles emails that don’t match any specific rules).
- Add policy statements by choosing Add new policy statement:
- Choose Deny for emails that don’t meet security requirements.
- Add condition: TLS Protocol Version select Less than and then select 1.2.
- Add conditions for any Email Add-Ons you’ve subscribed to, such as Spamhaus, Abusix, and so on.)
- Choose Create traffic policy.
Traffic policies are evaluated in a specific sequence:
- First, all
Denypolicy statements are evaluated in order. If any match, the email is immediately blocked and no further evaluation occurs. - If no
Denystatements match, allAllowpolicy statements are evaluated in order. Multiple statements within a policy are connected byORlogic. If any statement matches, the email is allowed. - Within each individual policy statement, multiple conditions are connected by
ANDlogic. All conditions must be true for the statement to match. - If no policy statements match (neither
DenynorAllow), the default action of the traffic policy (eitherAlloworDeny) is applied.
In this step, you’ll establish a robust policy that enforces strict TLS security protocols while harnessing the power of specialized email security add-ons such as Abusix Guardian Mail to preemptively identify and block potentially harmful messages before they can penetrate your system. In this traffic policy configuration, you’ll create two policy statements that work together to provide security and flexibility:
Default policy statement:
- Deny-by-default where all email traffic is initially blocked unless explicitly allowed by below policy statements
Policy statement 1:
- Allows emails if the recipient address is in a list called
Valid-Address
Policy statement 2 (with three conditions connected by AND):
- Must NOT be listed in Abusix Guardian Mail (
FALSEcondition) - The recipient address must NOT be in the
Invalid-Email-List - The TLS protocol version must be at least TLS 1.3
In basic terms, this policy will allow emails that either:
- Have recipients from an approved address list, or
- Meet all three security conditions (not deny-listed, not on the invalid list, and using secure TLS 1.3)


Step 6: Create a rule set
Rule sets define how your emails are processed after they pass through your traffic policy. In this example, the rule set establishes a sequential email processing workflow. First, you will perform email scanning (marking and segregating spam emails while allowing clean ones to proceed) and archiving outgoing messages, then finally delivering clean messages to recipients. To create a rule set:
- Open the Amazon SES console.
- Go to Mail Manager and choose Rule sets.
- Choose Create rule set.
- Enter a unique name for your rule set.
- On the rule set’s overview page, choose Edit, then choose Create new rule

Step 7: Create rules
After creating your rule set, you’ll need to add rules that define how your emails are processed. Follow these steps to create and configure your rules:
- On the rule set’s overview page, choose Edit, then Create new rule.
- In the Rule details sidebar, enter a unique name for your rule.
- Add conditions or exceptions as needed:
- Select Add new condition to specify what messages the rule applies to.
- Select EXCEPT in the case of and select Add new exception for exclusions.
- Configure actions by choosing Add new action.
- For multiple actions, use the up and down arrows to set the execution order.
- When finished creating your rules, choose Save rule set to apply your changes.
Rule 1: Scan and isolate malicious content
This rule targets emails flagged by Vade Advanced Email Security as potentially harmful. It applies to messages identified as scams, suspect content, phishing attempts, or containing malware. When a message is flagged as malicious, the rule marks it with a custom header, stores a copy in Amazon S3 for investigation, and prevents it from reaching recipients. An exception allows emails with Action required in the subject line to bypass this security check.
Use the following settings to create and configure Rule 1:
- Rule name: Scan and isolate
- Conditions:
- Property: Select Verdict (Vade Advanced Email Security).
- Operator: Select Equals.
- Value: Select scam, suspect, phishing, and malware.
- Actions:
- Add header: For Key, enter
X-vedacheckand for Value, enterfailed. - Write to S3: Enter the name of an S3 bucket to store the message for investigation.
- Drop: Stop processing the message.
- Add header: For Key, enter

Rule 2: Archive and send clean emails to recipients
This final rule processes messages that have successfully passed through the previous security checks. With no additional conditions, it forwards clean emails to their intended recipients, completing the secure email delivery workflow for the university’s communication system. Use the following settings to create and configure Rule 2:
- Rule name: SendEmail
- Action:
- Add header: For Key , enter
Add X-vedacheckwith a Value ofApproved. - Archive resource name: Select your Mail Manager archive (Email_Archive)
- Send to internet: Send email to intended recipient.
- Add header: For Key , enter

The workflow makes sure that:
- All outbound emails are securely archived
- Each email undergoes scanning
- Scan results are documented in email headers
- Clean emails are delivered to their intended recipients
Step 8 : Store password in AWS Secrets Manager for the ingress endpoint
Before creating an ingress endpoint, you need to set up a password in AWS Secrets Manager:
- Go to the AWS Secrets Manager console and choose Store a new secret.
- Select Other type of secret.
- Enter
passwordas the key and your desired password as the value. - For Encryption key: Use a custom KMS key (not AWS managed keys).
- KMS customer managed key (CMK) key policy for ingress endpoint. Replace
XXXXXXXXXXXwith your AWS account ID.
- KMS customer managed key (CMK) key policy for ingress endpoint. Replace
- Choose Next to proceed
- Enter a secret name and choose Edit permissions and update the resource policy. Replace
XXXXXXXXXXXwith your AWS account ID.
- Choose Next and create your secret

For step-by-step guidance, see the Developer guide for Ingress endpoints.
Step 9: Create an authenticated ingress endpoint
Now that you’ve created your traffic policy, rule set, and stored your credentials, you can create the ingress endpoint:
- In the Amazon SES console, choose Mail Manager and then choose Ingress endpoints.
- Choose Create ingress endpoint.
- Configure your endpoint:
- Select the Traffic policy you created earlier.
- Select the Rule set you created earlier.
- Enter a unique name for your endpoint.
- For authentication, select the Secret ARN you created in Secrets Manager.
- Choose Create ingress endpoint.
 After your ingress endpoint is created, note down the following details from the General details section:
After your ingress endpoint is created, note down the following details from the General details section:
- Amazon Resource Name (ARN):
arn:aws:ses:us-east-1:XXXXXXXXXXX:mailmanager-ingress-point/inp-XXXXXXXXXXXX - Username:
inp-XXXXXXXXXXXX - Host:
XXXXXXXXX.fips.wmjb.mail-manager-smtp.amazonaws.com(ARecord)
You’ll need these details when configuring your email client or application to send emails through this endpoint.

Step 10: Send email using an ingress endpoint
The following Python sample code can be executed from your local machine with the appropriate AWS credentials, but for this post you’ll run the script from the AWS CloudShell terminal from within the Amazon SES console. When running the sample Python code, the email will pass through an ingress endpoint and, if all policies are met, the email will be sent to the recipient’s email address.
Running the Python script in CloudShell
- Sign in to the console and open CloudShell.
- Create the script file and paste the following Python code into the editor.
- Paste the following Python code:
- Replace all placeholders
INGRESS_SERVER =XXXXXXXXXXX---fips---wmjb---mail-manager-smtp.amazonaws.com.rproxy.govskope.cais your ingress endpoint hostname.INGRESS_PORT= Supported ports: 25, 587INGRESS_USERNAME = inp-XXXXXXXXXXXXis your ingress endpoint username.- Recipient and sender=
XXXXXXXXXXX@domain.comis your verified sender and recipient email addresses.
- Save the file.
- Run the script:
- Verify the results:
- Check the recipient’s inbox for the email.
- Check the Mail Manager archive to confirm the message was archived.
To search the Mail Manager archive for the specific message sent by the Python script:
- Navigate to the Amazon SES console and choose Mail Manager.
- Under Email Archiving, choose the Search archive tab.
- Under Archive, select the archive you created and choose Search. This should return all the emails you have sent.

Clean up
Clean up your AWS environment by removing all resources created during this walkthrough, including Mail Manager configurations, S3 buckets, secrets, and any associated Lambda functions.
Conclusion
In this post, we’ve demonstrated the implementation of sophisticated traffic policies, multi-layered rule systems, and automated archiving capabilities—all seamlessly integrated into a scalable architecture. The ability of Amazon SES Mail Manager to enforce TLS requirements, conduct email scanning, and maintain searchable archives while providing programmatic access through ingress endpoints makes it an invaluable tool for organizations seeking to modernize their email infrastructure.As businesses continue to rely heavily on email communication, Amazon SES Mail Manager emerges as a powerful ally, helping organizations navigate the complexities of modern digital correspondence while ensuring rock-solid security, seamless compliance, and optimal efficiency.
References:
- Amazon SES Mail Manager Documentation
- Traffic policies and policy statements
- Rule sets and rules
- Email archiving
- Ingress endpoints
- Email Add Ons
- AWS Secrets Manager