- AWS›
- Security, Identity, and Compliance
Taiwan Data Privacy
Overview
The Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) is the primary legislation governing personal data protection in Taiwan. The Enforcement Rules of the PDPA provide further guidelines on interpretation and implementation of the PDPA.
The term “personal data” is defined in the PDPA to refer to information that may be used to directly or indirectly identify a natural person.
According to the PDPA, a data subject’s consent is required for the collection, processing and use of his/her personal data. The collection, processing and use of personal data must be carried out within the necessary scope of the specific purposes disclosed/notified to the data subject at the time of collection. The collection and processing of sensitive personal data is prohibited unless certain conditions are met. The PDPA also lists out the key principles that apply to the processing of personal data, the individual rights of data subjects in relation to their personal data, and the measures to be taken by a controller/processor to ensure the security of personal data.
Article 21 of the PDPA stipulates that non-governmental entities are restricted by central competent authorities from transferring personal data outside Taiwan if any of the following circumstances occurs: (i) where major national interests are involved; (ii) where an international treaty or agreement specifies otherwise; (iii) where the country receiving personal data lacks proper regulations governing the personal data protection so that it might harm the rights and interests of the data subject; or (iv) where the cross-border transfer of personal data is made through an indirect method for circumventing the application of the PDPA. In practice, in addition to the PDPA, respective competent government agencies may have detailed administrative rules or requirements for cross-border personal data transfer, and thus it is prudent for a non-governmental entity to confirm the legality with its supervisory authority before making any international transfer of personal data.
AWS is vigilant about your privacy and data security. Security at AWS starts with our core infrastructure. Custom-built for the cloud and designed to meet the most stringent security requirements in the world, our infrastructure is monitored 24x7 to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of our customer's data. The same world-class security experts who monitor this infrastructure also build and maintain our broad selection of innovative security services, which can help you simplify meeting your own security and regulatory requirements. As an AWS customer, regardless of your size or location, you inherit all the benefits of our experience, tested against the strictest of third-party assurance frameworks.
AWS implements and maintains technical and organizational security measures applicable to AWS cloud infrastructure services under globally recognized security assurance frameworks and certifications, including ISO 27001, ISO 27017, ISO 27018, PCI DSS Level 1, and SOC 1, 2, and 3. These technical and organizational security measures are validated by independent third-party assessors, and are designed to prevent unauthorized access to or disclosure of customer content.
For example, ISO 27018 is the first International code of practice that focuses on protection of personal data in the cloud. It is based on ISO information security standard 27002 and provides implementation guidance on ISO 27002 controls applicable to Personally Identifiable Information (PII) processed by public cloud service providers. This demonstrates to customers that AWS has a system of controls in place that specifically address the privacy protection of their content.
These comprehensive AWS technical and organizational measures are consistent with the goals of the PDPA to protect personal data. Customers using AWS services maintain control over their content and are responsible for implementing additional security measures based on their specific needs, including content classification, encryption, access management and security credentials.
As AWS does not have visibility into or knowledge of what customers are uploading onto its network, including whether or not that data is deemed subject to the PDPA, customers are ultimately responsible for their own compliance with the PDPA and related regulations. The content on this page supplements the existing Data Privacy resources to help you align your requirements with the AWS Shared Responsibility Model when you store and process personal data using AWS services.

Page topics
FAQs
Open allUnder the AWS Shared Responsibility Model, AWS customers retain control of what security they choose to implement to protect their own content, platform, applications, systems and networks, no differently than they would for applications in an on-site data center. Customers can build on the technical and organizational security measures and controls offered by AWS to manage their own compliance requirements. Customers can use familiar measures to protect their data, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication, in addition to AWS security features like AWS Identity and Access Management.
When evaluating the security of a cloud solution, it is important for customers to understand and distinguish between:
- Security measures that AWS implements and operates - "security of the cloud", and
- Security measures that customers implement and operate, related to the security of their customer content and applications that make use of AWS services - "security in the cloud"
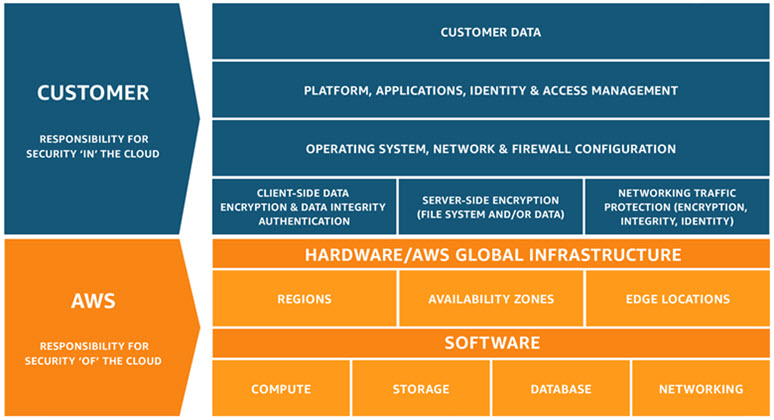
Customers maintain ownership and control of their customer content and select which AWS services process, store and host their customer content. AWS does not have visibility into customer content and does not access or use customer content except to provide the AWS services selected by a customer or where required to comply with the law or a binding legal order.
Customers using AWS services maintain control over their content within the AWS environment. They can:
- Determine where it will be located, for example the type of storage environment and geographic location of that storage.
- Control the format of that content, for example plain text, masked, anonymized or encrypted, using either AWS provided encryption or a third-party encryption mechanism of the customer’s choice.
- Manage other access controls, such as identity access management and security credentials.
- Control whether to use SSL, Virtual Private Cloud and other network security measures to prevent unauthorized access.
This allows AWS customers to control the entire life-cycle of their content on AWS and manage their content in accordance with their own specific needs, including content classification, access control, retention and deletion.
AWS data centers are built in clusters in various locations around the world. We refer to each of our data center clusters in a given location as a "Region."
AWS customers choose the AWS Region(s) where their content will be stored. This allows customers with specific geographic requirements to establish environments in the location(s) of their choice.
Customers can replicate and back up content in more than one Region, but AWS does not move customer content outside of the customer’s chosen Region(s), except to provide services as requested by customers or comply with applicable law.
The AWS data center security strategy is assembled with scalable security controls and multiple layers of defense that help to protect your information. For example, AWS carefully manages potential flood and seismic activity risks. We use physical barriers, security guards, threat detection technology, and an in-depth screening process to limit access to data centers. We back up our systems, regularly test equipment and processes, and continuously train AWS employees to be ready for the unexpected.
To validate the security of our data centers, external auditors perform testing on more than 2,600 standards and requirements throughout the year. Such independent examination helps ensure that security standards are consistently being met or exceeded. As a result, the most highly regulated organizations in the world trust AWS to protect their data.
Learn more about how we secure AWS data centers by design by taking a virtual tour »
Customers can choose to use any one Region, all Regions or any combination of Regions. Visit the AWS Global Infrastructure page for a complete list of AWS Regions.
The AWS Cloud infrastructure has been architected to be one of the most flexible and secure cloud computing environments available today. Amazon's scale allows significantly more investment in security policing and countermeasures than almost any large company could afford on its own. This infrastructure is comprised of the hardware, software, networking, and facilities that run AWS services, which provide powerful controls to customers and APN Partners, including security configuration controls, for the handling of personal data. More details on the measures AWS puts in place to maintain consistently high levels of security can be found in the AWS Overview of Security Processes Whitepaper.
AWS also provides several compliance reports from third-party auditors who have tested and verified our compliance with a variety of security standards and regulations - including ISO 27001, ISO 27017, and ISO 27018. To provide transparency on the effectiveness of these measures, we provide access to the third party audit reports in AWS Artifact. These reports show our customers and APN Partners, who may act as either data controllers or data processors, that we are protecting the underlying infrastructure upon which they store and process personal data. For more information, visit our Compliance Resources.