AWS Storage Blog
Protect Amazon Aurora DSQL clusters using AWS Backup
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are migrating mission-critical databases to the cloud for better performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Amazon Aurora DSQL, a serverless distributed SQL database, is purpose-built for always available applications with virtually unlimited scale, the highest availability, and zero infrastructure management. As customers adopt Aurora DSQL, ensuring comprehensive data protection becomes critical to maintaining business continuity. Robust backup strategies are essential—not only to guard against accidental deletion and ensure compliance across geographies, but also to support point-in-time recovery in the event of logical corruption or operational errors.
As these workloads grow in scale and geographic reach, backup management can become more complex. Organizations running Aurora DSQL across multiple AWS Regions to support global workloads need an efficient approach to coordinate backups, maintain data integrity, and meet compliance requirements. A centralized backup solution like AWS Backup helps streamline these operations. AWS Backup integrates natively with Aurora DSQL and over 20 other AWS services, providing comprehensive backup and restore capabilities from a centralized platform. AWS Backup’s cross-Region and cross-account backup and logically air-gapped vault features protect against localized failures or account compromise, enhance compliance, and make sure of business continuity. This automated approach streamlines backup management and minimizes potential downtime during recovery scenarios.
Given the critical role of backup in distributed database environments, a well-designed backup strategy is essential. In the following sections, we’ll walk you through how you can protect your Aurora DSQL clusters using AWS Backup.
Solution overview
In this post, we demonstrate how to back up and restore Amazon Aurora DSQL clusters using AWS Backup, which supports both single-Region and multi-Region deployments. We’ll walk through creating both on-demand and scheduled backups, as well as restoring clusters in either configuration. For scheduled backups, you can define settings such as frequency, retention, and optional cross-Region copy rules—particularly useful for multi-Region clusters to enhance resilience. When a restore is needed, you can initiate the process directly from AWS Backup by specifying the appropriate parameters for your Aurora DSQL clusters.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are necessary to complete this solution:
- An AWS account is needed for this tutorial. For more information on using AWS Backup for the first time, view the AWS Backup documentation.
- One or more Aurora DSQL clusters. For the pricing of Aurora DSQL clusters, refer to the Aurora DSQL pricing page. For AWS Backup pricing, refer to the AWS Backup pricing page.
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles used by AWS Backup to create a backup of the Aurora DSQL clusters.
- If a subsequent role is not created, then the default IAM role can be used: AWSBackupDefaultRole.
Walkthrough
The following steps walk you through how to back up and restore Aurora DSQL clusters.
Getting started with AWS Backup from the AWS Management Console
Go to the AWS Backup console. If this is your first time using AWS Backup, then you need to opt-in to the resource settings under My account as shown in the Figure 1.
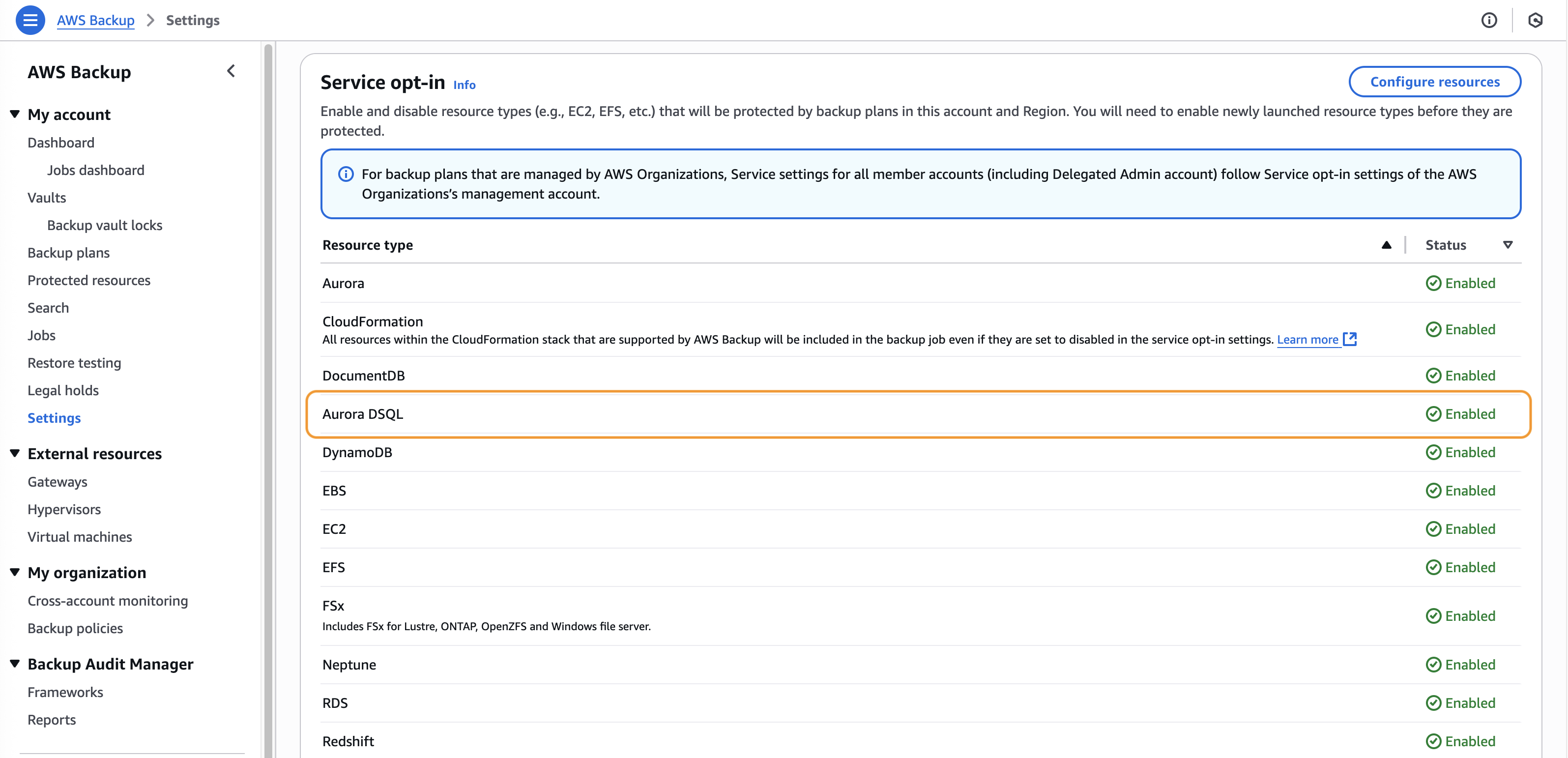 Figure 1: Opt-in to backing up Aurora DSQL service from account settings
Figure 1: Opt-in to backing up Aurora DSQL service from account settings
To take backups of your Aurora DSQL clusters, you can create a backup plan, which takes backups periodically at a defined schedule, or take an on-demand backup. AWS Backup supports the backups of both single-Region and multi-Region clusters.
AWS Backup does not automatically replicate backups across AWS Regions. Therefore, when managing multi-Region Aurora DSQL clusters, you need to maintain backups in all participating Regions. We recommend creating backups in a designated primary Region and then copying them to the other Regions within the cluster. This approach ensures backup availability across all Regions and simplifies management. You can configure automated cross-Region copies as part of your scheduled backup plan (as demonstrated in the steps below), or you can initiate an on-demand copy at the time of restore. Scheduled copies help achieve a shorter recovery time objective (RTO), as backups are already available in the target Regions. In contrast, on-demand copies can help reduce storage costs by deferring copy until a restore is actually required.
Create scheduled backups
You can create backups for single-Region and multi-Region clusters using the same process. To implement scheduled backups, create your backup plan by going to the Backup plan tab, as seen in Figure 2.
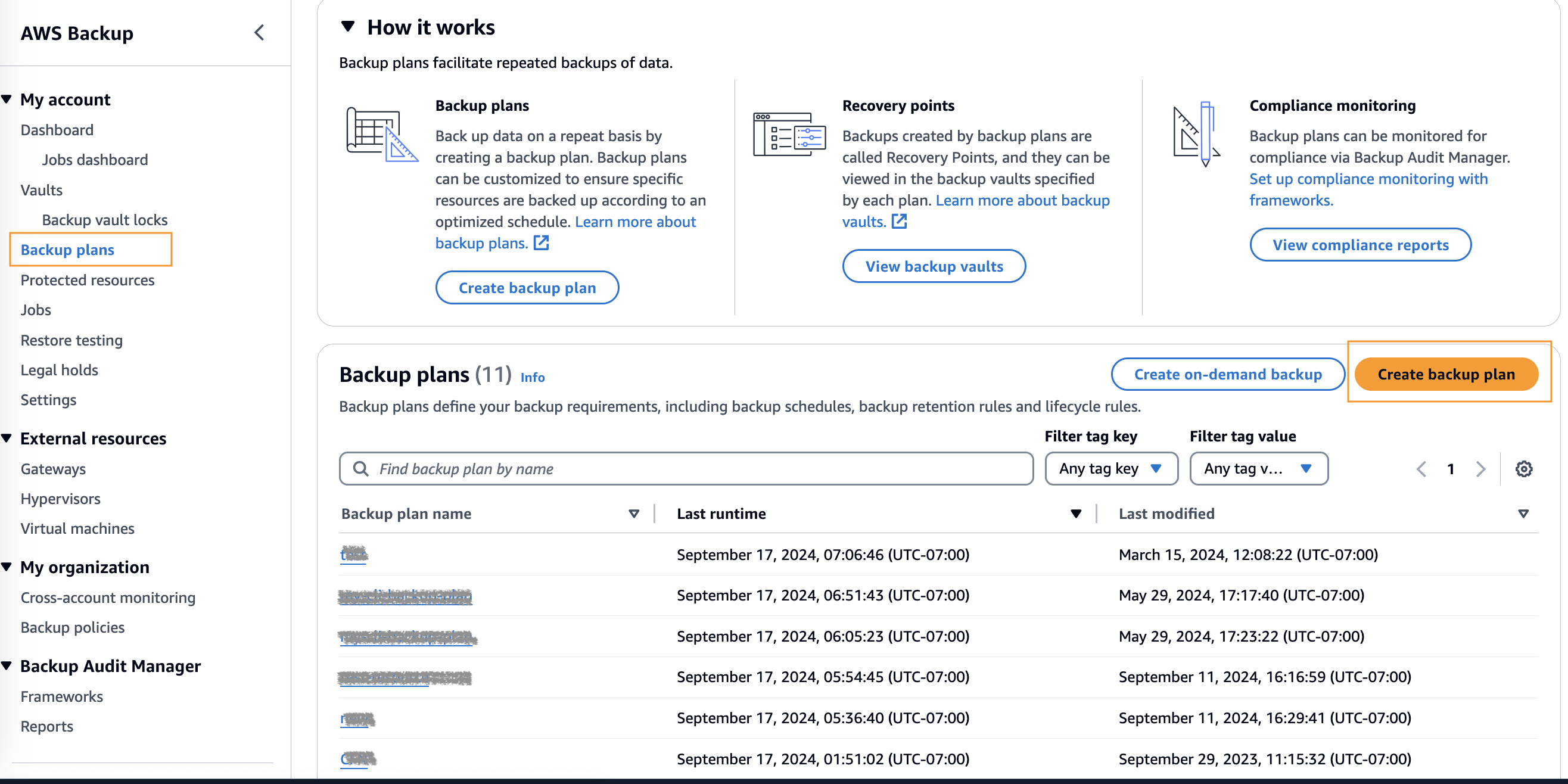
Figure 2: Go to the Backup plans tab from the left hand side of AWS Backup console
Choose Create backup plan, and you are directed to the Create backup plan workflow, as shown in Figure 3.
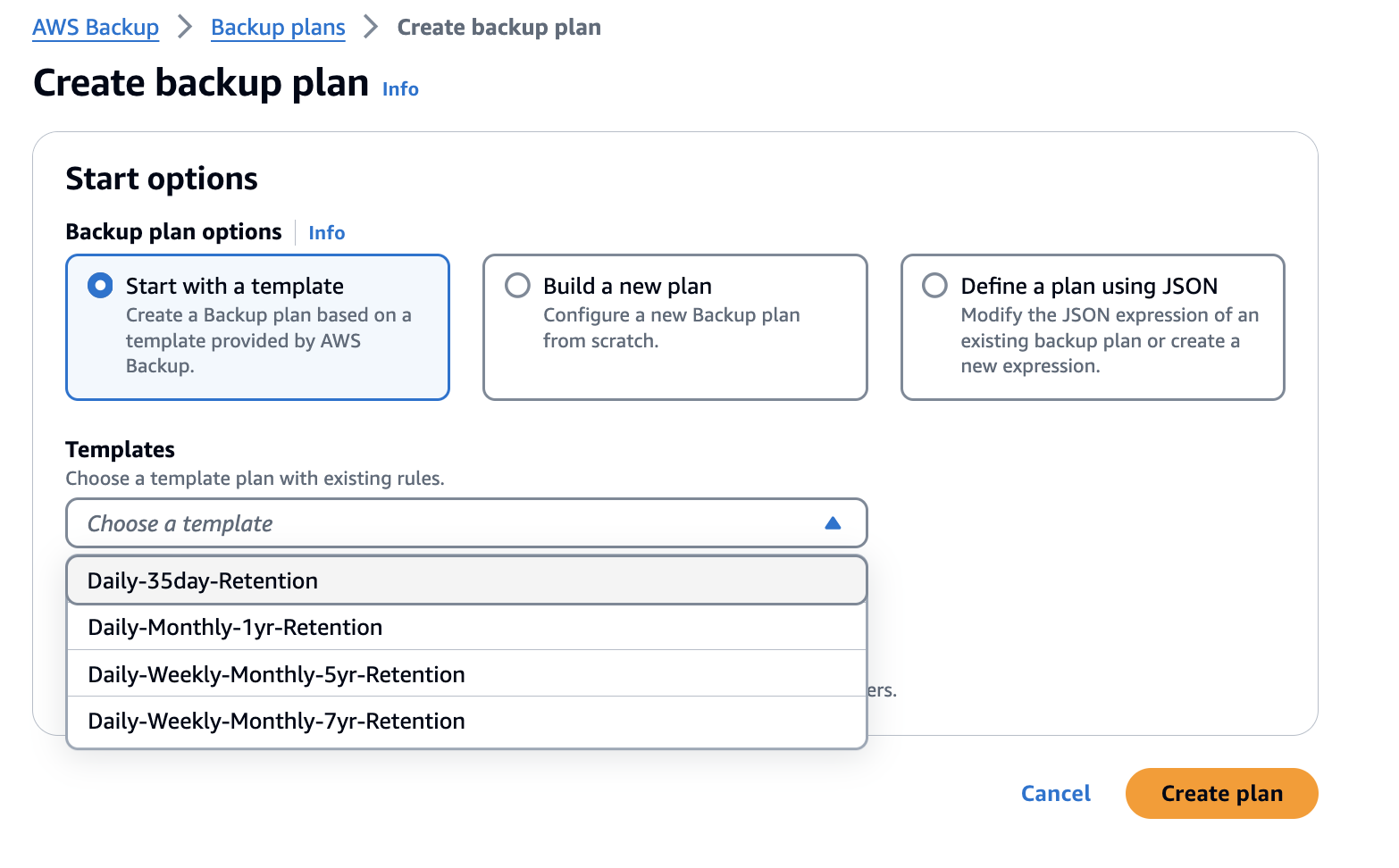 Figure 3: Landing page for Create backup plan workflow
Figure 3: Landing page for Create backup plan workflow
Choose Start with a template, use the Daily-35day-Retention template, and specify a name for your backup plan, as shown in Figure 4.
This default daily template takes backups daily and retains them for 35 days. If you have different frequency or retention requirements, you can choose to edit the DailyBackups rule template, as shown in the following figure.
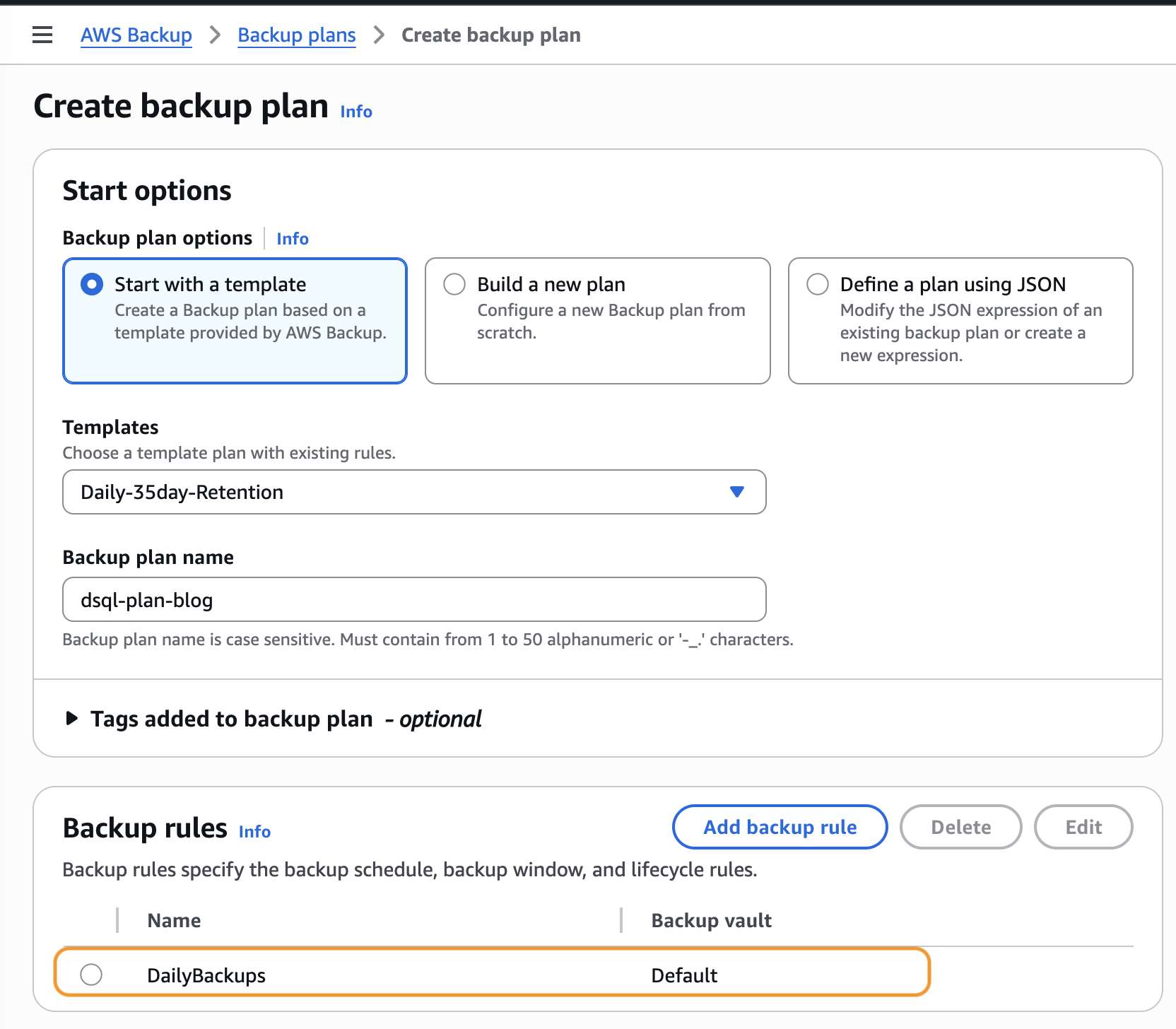 Figure 4: Choose Daily-35day-Retention template
Figure 4: Choose Daily-35day-Retention template
You can choose to create backup copies in another AWS Region or account to provide additional redundancy. For multi-Region clusters, you must have identical copies of backups in each AWS Region that the multi-Region cluster spans to perform a multi-Region cluster restore. As a result, it is strongly recommended to add a copy action in your backup rule to copy the backup to the second Region of your multi-Region clusters. This makes sure that your multi-Region clusters are ready to be restored in a data loss event. To do that, choose the backup rule DailyBackups, choose Edit, then Copy to destination. If you want additional security, you can choose a logically air-gapped (LAG) vault as the destination vault. Logically air-gapped vaults store immutable backup copies that are locked by default and isolated with encryption using AWS owned keys, improving your recovery time and defense posture.
In Figure 5, we copy our backup from United States (N. Virginia) to United States (Oregon) as our multi-Region cluster spans these two Regions.
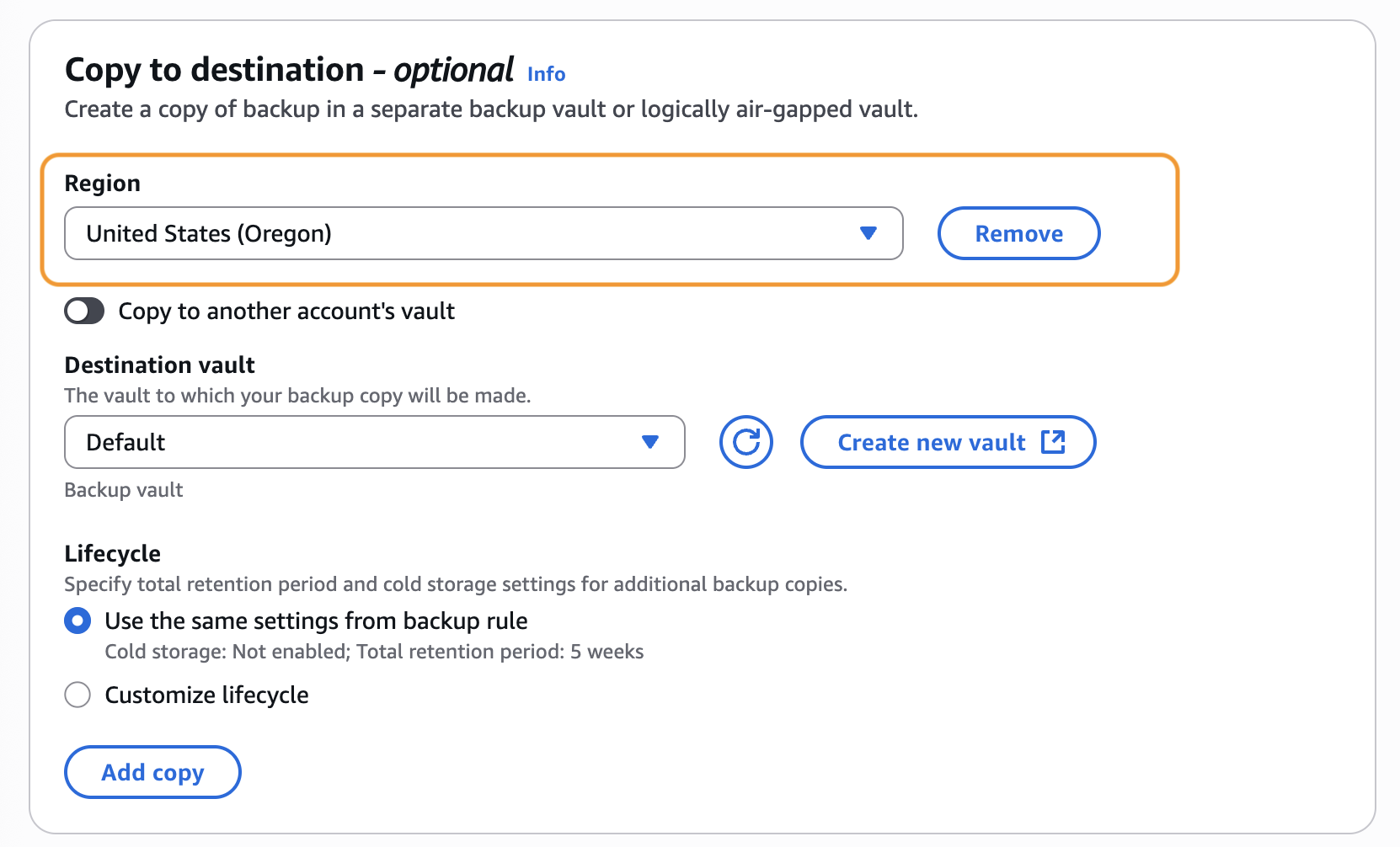 Figure 5: Create copy rule to another AWS Region for your multi-Region cluster backup
Figure 5: Create copy rule to another AWS Region for your multi-Region cluster backup
After saving the backup rule, you should observe the Create backup plan screen showing the summary of your choices. Choose the Create Backup Plan button.
You should observe a green banner signaling that your backup plan has been created successfully, as shown in Figure 6. Then, you are directed to assign your resources to backup. You can choose Aurora DSQL clusters from the specific resource type, or use a tag.
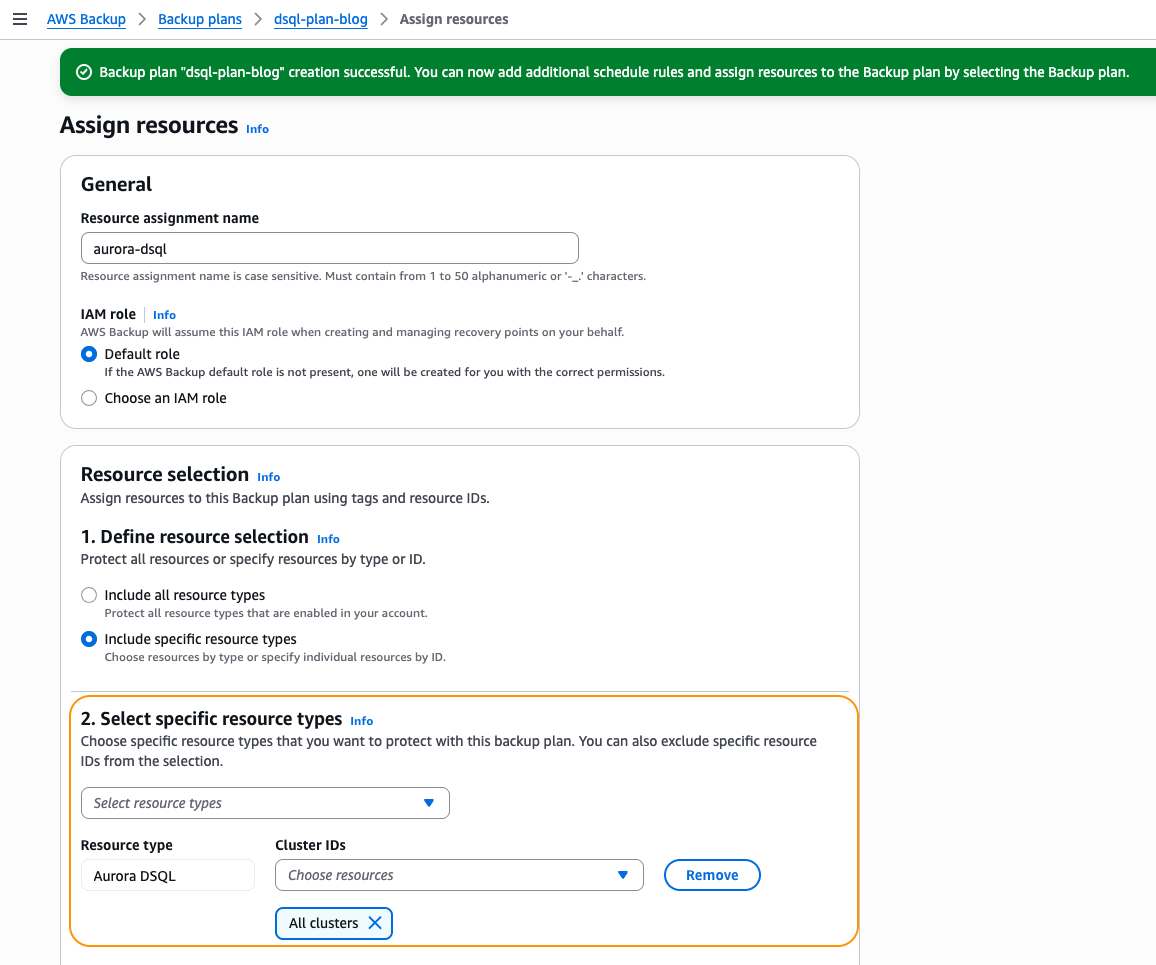 Figure 6: Assign resources workflow as part of creating your backup plan
Figure 6: Assign resources workflow as part of creating your backup plan
You can refine the choice further by using tags or choosing the specific Aurora DSQL clusters that you want to protect. Once you have completed the resource selection, choose Assign resources.
You have finished creating a backup policy to protect your Aurora DSQL from accidental deletion, corruption, or other data loss events. You should observe a green banner signaling that your resource assignment has been created successfully, and a summary of your plan should be shown as in Figure 7.
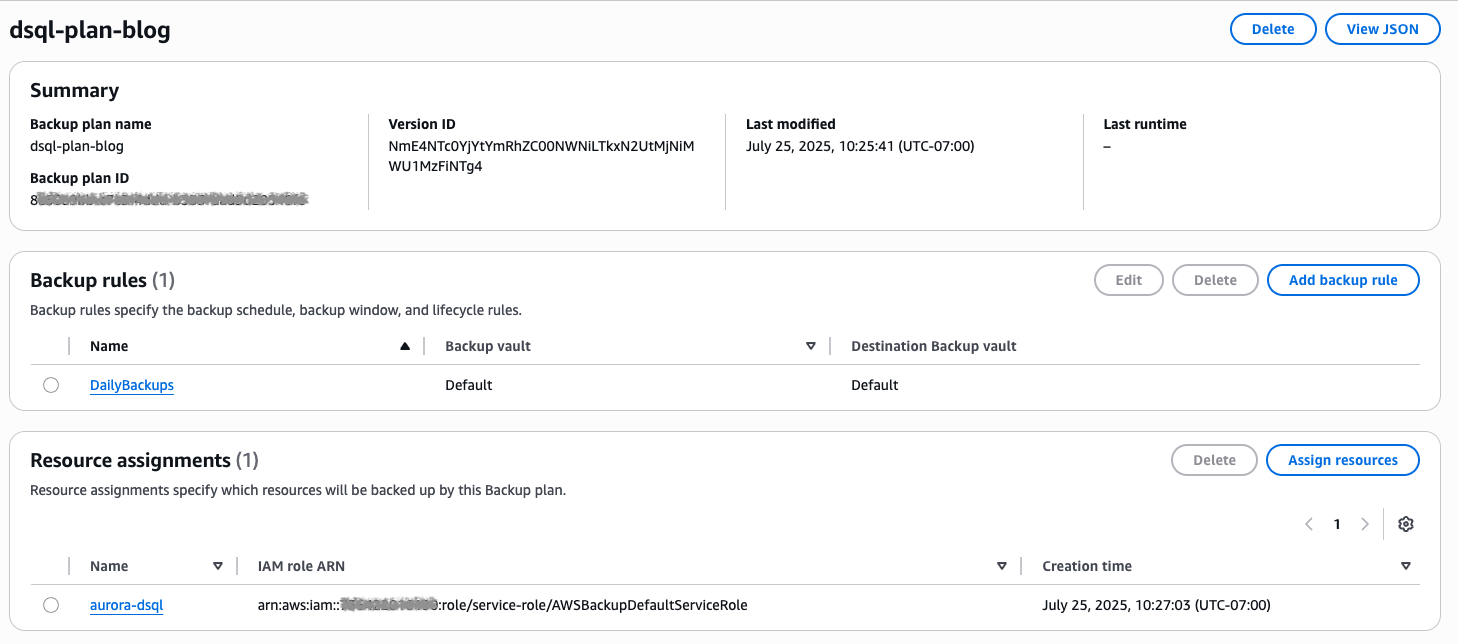 Figure 7: Summary of backup plan with Backup rules and Resource assignments
Figure 7: Summary of backup plan with Backup rules and Resource assignments
Restore the backup of your Aurora DSQL clusters
AWS Backup supports the restore of both single-Region and multi-Region Aurora DSQL clusters using the AWS Backup console or API. Even though the steps are the same, there are some differences in the restore parameters required for the multi-Region cluster restore. In the following steps, we will go through the restore process for both single-Region and multi-Region clusters.
To initiate any restore, go to Vaults, or Protected resources. Then, choose the recovery points you want restore, and choose Action then Restore.
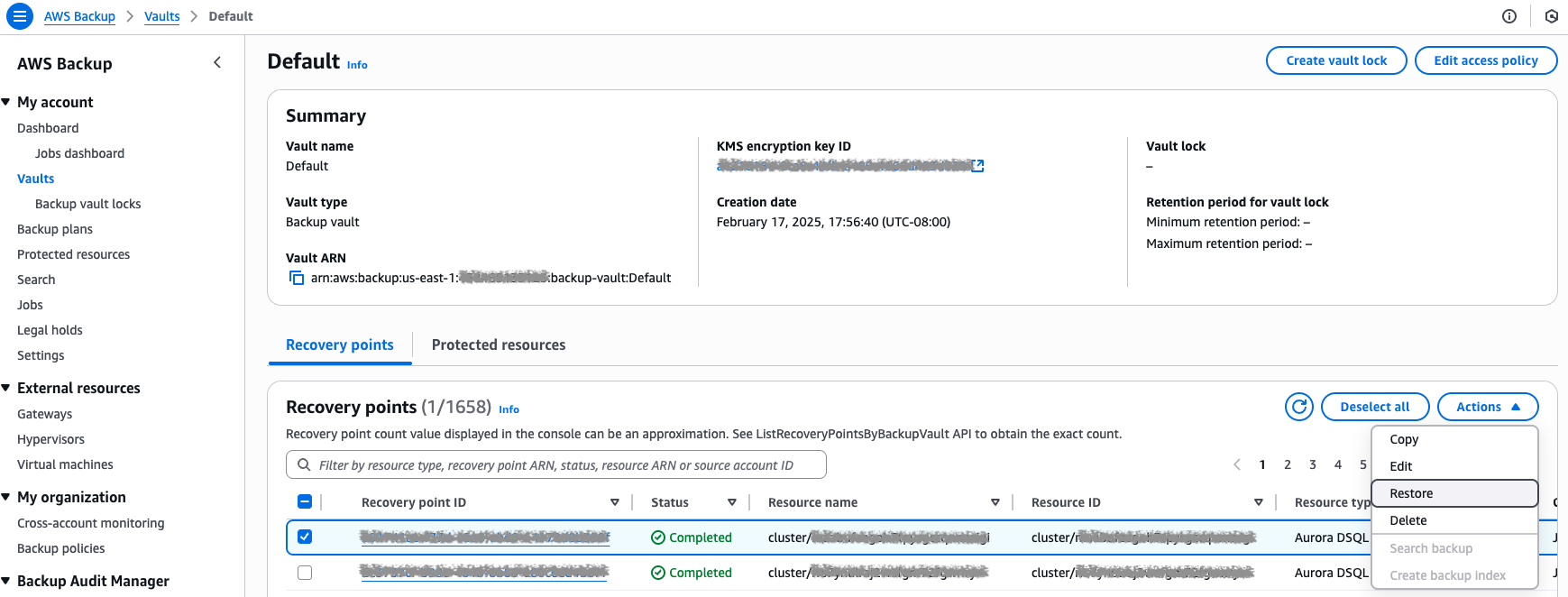 Figure 8: Choose the recovery point to restore
Figure 8: Choose the recovery point to restore
Single-Region cluster restore
For single-Region cluster restores, you can configure both encryption and deletion protection settings. By default, the restored Aurora DSQL cluster is encrypted using an AWS owned-key. However, if your organization requires more control, you can choose to encrypt the cluster with a customer-managed key from your AWS account. To do this, simply check the Customer encryption settings box and select the appropriate key. Additionally, deletion protection is enabled by default to help prevent accidental deletion of the restored cluster. Once you’ve configured your restored cluster settings, click Restore.
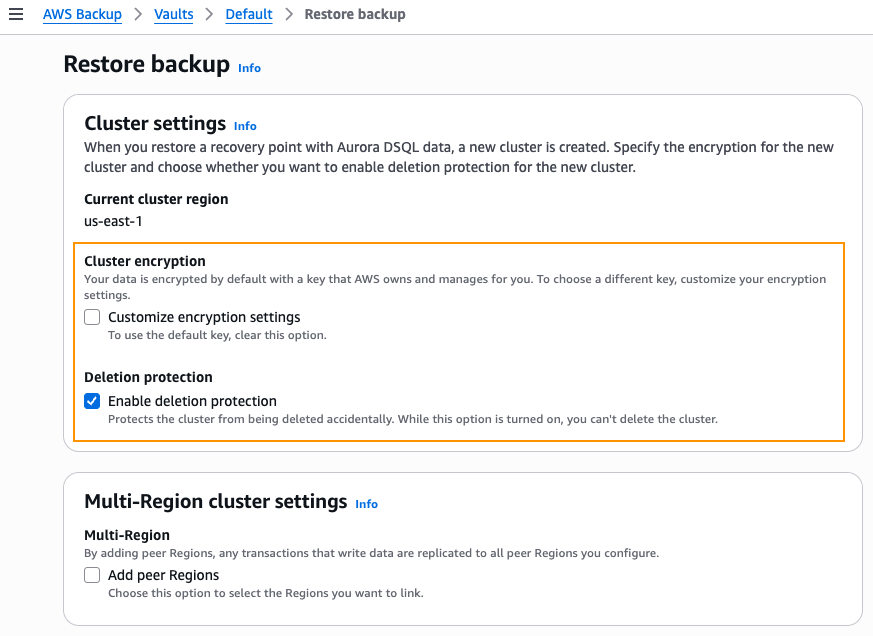
Figure 9: Single-Region restore configuration
Multi-Region cluster restore
There are parameters specific to a multi-Region cluster restore – peer Regions and witness Region. To change these settings, choose Add peer Regions, and choose the peer Region for your multi-Region cluster, as shown in the Figure 10.
Similar to single-Region cluster restores, you can configure encryption and deletion protection settings for each cluster within a multi-Region Aurora DSQL cluster. This includes the ability to specify a different AWS KMS key for each peer cluster, allowing greater flexibility to meet region-specific security or compliance requirements.
If you don’t already have an identical copy of the first Region’s backup in the peer Region, then your multi-Region restore fails. If you didn’t have a copy rule that copied the backup to the second Region, then create a copy now before starting the restore.
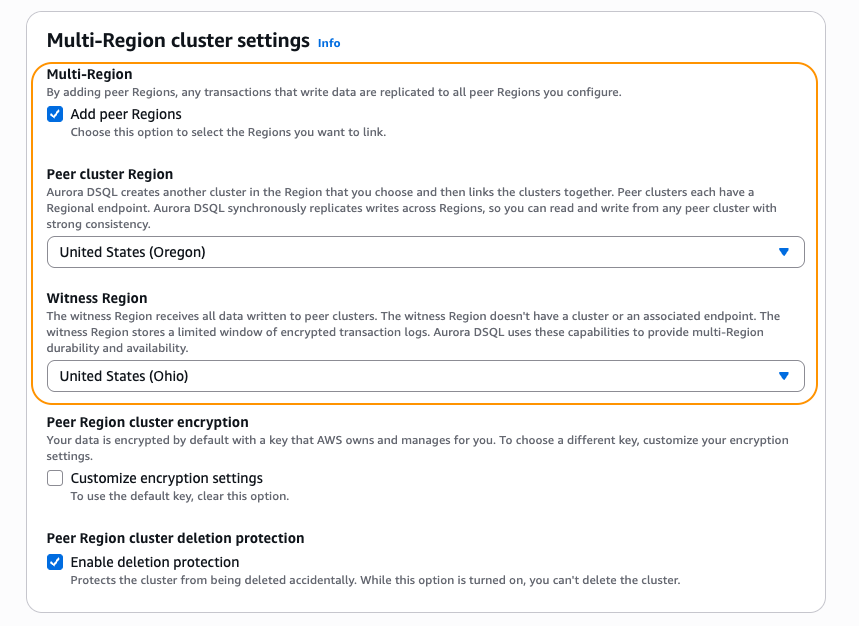
Figure 10: Multi-Region restore configuration
AWS Backup orchestrates the restores of your multi-Region cluster in both AWS Regions (the Region where the restore is started, and the peer Region) and links your restored clusters to create a multi-Region cluster, as shown in the following figure. To view the restored cluster, navigate to the Aurora DSQL console or API.
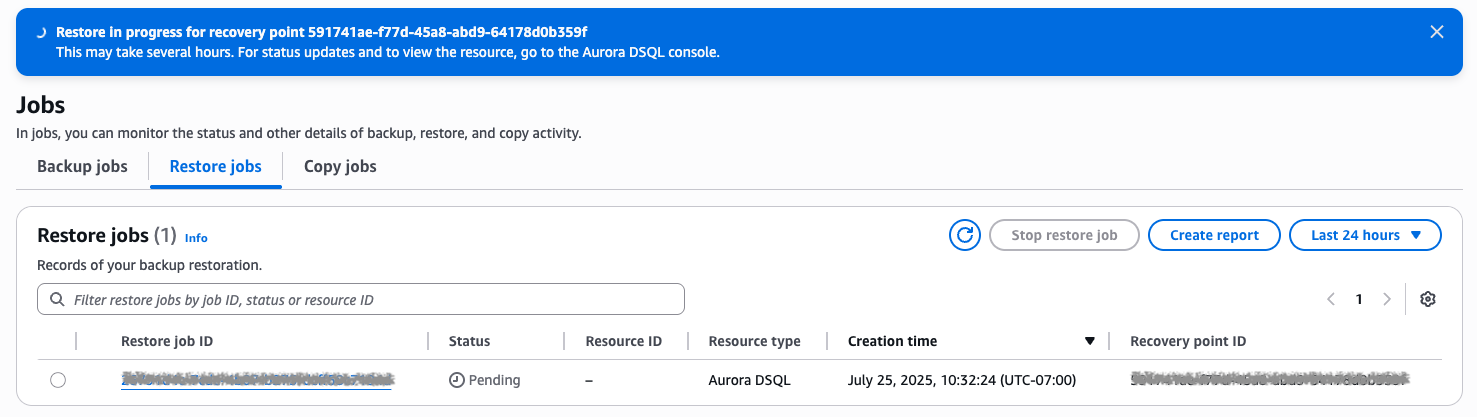 Figure 11: Restore job status
Figure 11: Restore job status
Cleaning up
To avoid incurring future costs, delete the backups if you no longer need them.
Conclusion
In this post, we walked through using AWS Backup to protect your Amazon Aurora DSQL clusters using the AWS console in a few steps. You can now create backup policies to protect Aurora DSQL clusters and restore both single Region and multi-Region clusters.
Effective backup and restore strategies are essential for maintaining the availability and integrity of your Aurora DSQL clusters, particularly in globally distributed environments. By leveraging AWS Backup’s native integration and features like automated cross-Region copying, you can simplify backup management while meeting your organization’s compliance and recovery goals. Whether managing single-Region or multi-Region clusters, following these best practices ensures your critical data stays protected and your business remains resilient.
To learn more about AWS Backup, visit the AWS Backup Developer Guide. If you have questions or comments, leave them in the comment section.