AWS Cloud Operations Blog
Optimize querying AWS CloudTrail logs with partitioning in Amazon Athena
Organizations leveraging AWS CloudTrail to audit API access encounter a common challenge: CloudTrail data volume grows proportionally with AWS infrastructure expansion. A multi-account AWS organization generating millions of API calls daily can quickly amass terabytes of CloudTrail logs. When security teams conduct incident investigations or account activity audits, querying these logs in Amazon Athena becomes resource-intensive and time-consuming, as Athena must scan the entire table for each query. The AWS documentation for Athena also shows how to manually partition CloudTrail logs.
AWS CloudTrail provides comprehensive API activity tracking across AWS environments for governance and auditing purposes, centralizing activity records. Amazon Athena, a serverless interactive query service, enables SQL-based analysis of Amazon S3 data without infrastructure management requirements, following a pay-per-query pricing model.
In this post, we’ll introduce an automated solution for creating and managing partitioned tables in Athena, enabling reduced query costs and accelerated security investigations. For example, when investigating suspicious activity from a specific account within the past week, Athena will scan only the relevant partitions containing that account’s recent data, rather than the entire dataset.
Solution Overview
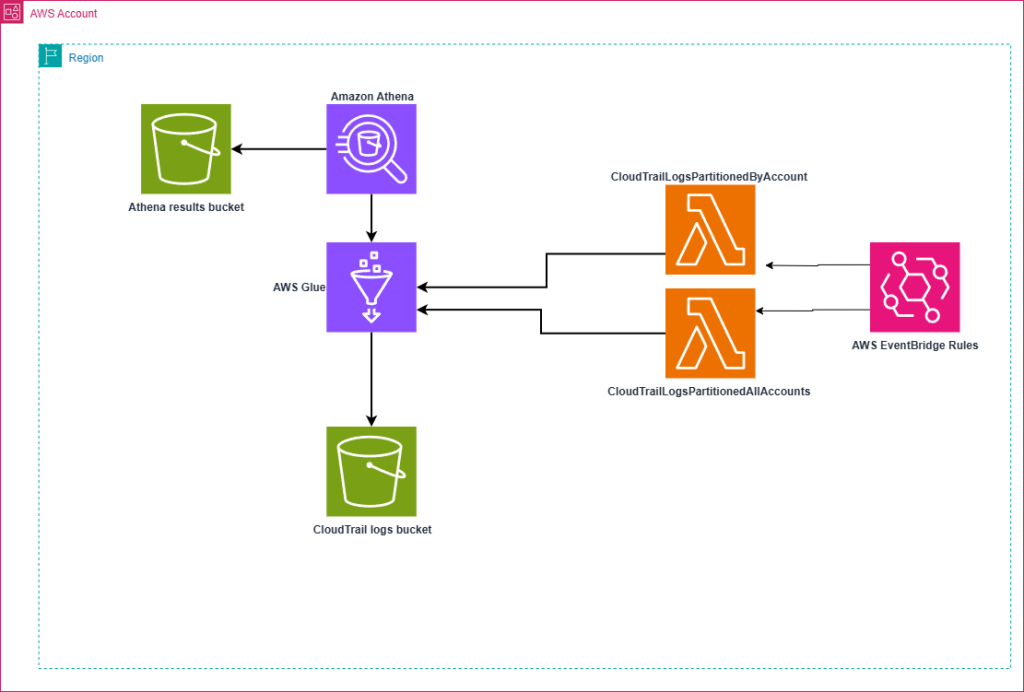
Figure 1: architecture diagram
The solution implements two Lambda functions to optimize querying CloudTrail logs. The CloudTrailLogsPartitionedByAccount function analyzes the CloudTrail logs bucket and creates dedicated Athena tables (e.g., trail_123456789012) for each discovered AWS account. The function automatically creates corresponding tables with Region and date partitioning as new accounts are added, enabling team-specific trail sharing and account-specific log analysis.
The CloudTrailLogsPartitionedAllAccounts function maintains a consolidated table (all_accounts_trail) containing logs from the entire AWS organization. This unified table, partitioned by account ID, Region, and date, updates automatically with organizational changes, facilitating cross-account investigations and organization-wide activity analysis through unified queries.
Both functions utilize partition projection and execute daily table updates to accommodate new accounts, ensuring Athena tables remain synchronized with organizational structure while maintaining optimal query performance and eliminating manual partition management requirements.
The solution needs the CloudTrail S3 bucket and prefix as an input. The prefix differs between organizational trails and account-level trails. For organizational trails, the format is ORG_ID/AWSLogs/ORG_ID where ORG_ID is the AWS Organization ID. For account-level trails, the prefix is AWSLogs/. If you have a custom prefix or want to validate if one exists, you can use the below AWS CLI command (replace TRAIL_NAME with the name of your trail):
aws cloudtrail describe-trails --trail-name-list TRAIL_NAME
If the response doesn’t include the field S3KeyPrefix then you are using the default prefix. Otherwise, add your prefix to the default prefix, e.g., PREFIX/ORG_ID/AWSLogs/ORG_ID.
Walkthrough
Now we will go over the high-level steps to optimize CloudTrail queries with partitioned Athena tables:
- Deploy CloudFormation Template: Initialize a new stack using the provided template, which configures Lambda functions, IAM roles, Glue database, and Athena named queries.
- Query CloudTrail using Athena: Access the Athena console to analyze CloudTrail logs using predefined or custom queries.
Prerequisites
Ensure the following requirements are met before deployment:
- Sufficient permissions to deploy the CloudFormation template
- Configured CloudTrail trail
- Configured Amazon Athena query result location.
- Permissions to access the S3 buckets for CloudTrail logs and Athena query results.
Step 1: Deploy the CloudFormation template
- Download the CloudFormation template.
- Access the AWS CloudFormation console and create a new stack by selecting With new resources (standard). Choose Upload a template file, upload the template, and proceed.
- Assign a descriptive stack name (e.g.,
cloudtrail-athena-partitioner). - Enter your CloudTrail bucket name (e.g.,
aws-controltower-logs-123456789012-us-east-1) and the appropriate prefix (AWSLogs/ORORG_ID/AWSLogs/ORG_ID). - Specify the Athena results bucket from the Athena settings page under query result location. Enter the bucket name without the s3:// prefix.
- Optionally customize the Athena database name from the default
ct-central, then select Next. - Acknowledge the IAM resource creation permission under Capabilities.
- Review and submit the stack configuration.
- Upon stack creation completion, the Lambda functions will initiate automatic Athena table management.
Step 2: Query CloudTrail logs with Athena
- Access the Amazon Athena console and select the specified database (default: ‘ct-central’).
- Navigate to Saved Queries in the Athena console menu to access predefined queries.
- Select Find most frequent console users to execute a sample query analyzing AWS console login frequency by user
- Execute the query to observe efficient partition scanning, resulting in faster results and reduced costs compared to unpartitioned tables. Results display user ARN and console login frequency.
Cost Considerations
This solution creates 2 Lambda functions, each invoked once per day. The Lambda functions runtime may differ between different accounts/ environments. Please monitor the functions’ runtime to understand the expected cost. Lambda pricing can be seen in the Lambda pricing page. As you run Athena queries, you will be incurred additional charges for the queries. Please see the pricing for Athena in the Athena pricing page.
Cleaning Up
To avoid ongoing charges, delete the deployed CloudFormation stack.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we demonstrated how to optimize CloudTrail log analysis by automating partitioned Athena tables. The solution reduces costs through optimized data scanning and accelerates security investigations with both per-account and consolidated views. The included predefined queries help teams start investigating common scenarios immediately, while serving as templates for custom queries. Get started today by implementing this solution in your AWS environment and optimize your Athena queries against CloudTrail logs.