Migration & Modernization
Beyond the Monolith: Structured Strategies for Database Modernization
Monolithic databases have long been a cornerstone of enterprise applications, but as organizations scale and adopt cloud-native architectures, these databases increasingly become bottlenecks. A structured approach to modernizing these monolithic databases addresses increased cost, scalability constraints, architectural rigidity, and performance degradation that prevent independent deployment and rapid innovation.
Organizations embarking on cloud migration often discover that while they’ve successfully containerized applications or adopted microservices, a shared monolithic database continues to create dependencies that prevent independent deployment, efficient scaling, and rapid innovation.
Working with customers through the AWS Migration Acceleration Program (MAP) has revealed common patterns. Teams migrate applications to AWS, modernize their application tier, but struggle with database decomposition due to its complexity.
Overcoming these complexity challenges delivers substantial benefits:
- Enhanced business agility – Teams can deploy changes to individual services with greater autonomy and less cross-organizational friction, significantly reducing time-to-market for new features.
- Optimized performance – Purpose-built databases tailored to specific workloads deliver better performance. A high-traffic customer service can use Amazon DynamoDB for millisecond latency, while a reporting service leverages Amazon Redshift for complex analytics.
- Improved cost management – Independent scaling of databases based on actual workload reduces over-provisioning. Organizations can transition from costly proprietary licenses to open-source alternatives, and right-size each database independently for optimal cost efficiency.
- Innovation enablement – Adopting purpose-built databases for specific workloads unlocks new capabilities. Teams can leverage the best database for their use case rather than forcing all workloads into a single database engine.
Assessing your database for decomposition
Before embarking on your database decomposition journey, conducting a comprehensive assessment to understand your database’s current state and building a business case can help set the foundation for success. This assessment phase aligns with discovery and planning activities in the MAP.
Using the AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) to analyze schema complexity, tables, stored procedures, triggers, and functions provides visibility into your database structure. AWS Transform offers AI-powered assessment capabilities that analyze and generate assessments and readiness reports for modernization planning.
Evaluating dependencies between database objects through automated assessment reports from AWS SCT, AWS Transform, third-party database discovery tools, or native database metadata queries reveals the interconnections that influence decomposition decisions. Analyzing access patterns using Oracle Automatic Workload Repository (AWR) or PostgreSQL pg_stat_statements helps identify query frequency and resource consumption patterns.
As well as highlighting the benefits to the organization within the business case, there is also a need to compare current database licensing and infrastructure costs against projected AWS costs. Consider license optimization through open-source alternatives like Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition. AWS offers the Optimization and Licensing Assessment (OLA) to help organizations analyze their current licensing costs and identify optimization opportunities during migration planning. Evaluating technical risks including data consistency and performance implications ensures informed decision-making.
A structured approach to database decomposition
The APG guide provides a systematic framework centered around four main implementation areas. This structured approach which has been refined through numerous customer engagements, helps organizations navigate the complexity of database decomposition while minimizing risk.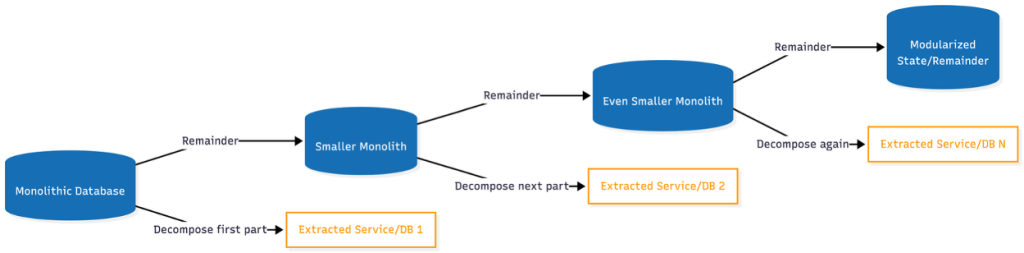
Figure 1: Database decomposition implementation areas – diagram showing the four areas and how they interconnect
1. Controlling database access
The journey begins by establishing controlled access to your monolithic database. The database wrapper service pattern creates a facade that becomes the only authorized way to access the database. This prevents further uncontrolled growth while providing visibility into access patterns.
The implementation is straightforward: create a lightweight service layer that mirrors existing database functionalities, systematically redirect all access through this wrapper, and use it as a centralized monitoring point. The wrapper prevents schema proliferation, establishes clear ownership boundaries, and provides the foundation for future decomposition.
For systems primarily used for analytics and reporting, the Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) pattern creates separate read-optimized data stores. This isolates reporting systems from decomposition impacts, allowing them to continue operations while you transform the primary database.
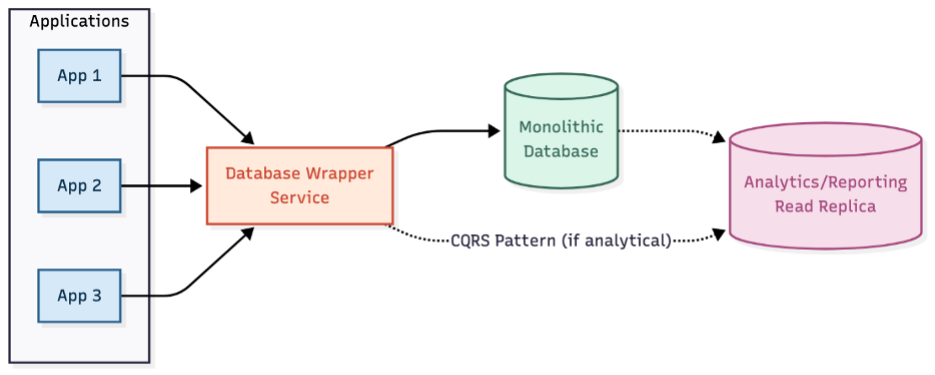 Figure 2: Database wrapper service pattern – diagram showing how the wrapper sits between applications and the monolithic database
Figure 2: Database wrapper service pattern – diagram showing how the wrapper sits between applications and the monolithic database
2. Analyzing cohesion and coupling
Understanding how database components interact is crucial for identifying natural break points. The guide provides a framework for analyzing coupling patterns (implementation, temporal, deployment, and domain coupling) and cohesion patterns (functional, sequential, and communicational cohesion).
Tools like SchemaSpy, CAST Imaging, and database profiling tools (Oracle AWR, PostgreSQL pg_stat_statements) help visualize relationships and identify self-contained tables. The guide includes a coupling-cohesion matrix that identifies which tables are easiest to decouple—tables in the high cohesion, low coupling quadrant becomes your initial decomposition candidates.
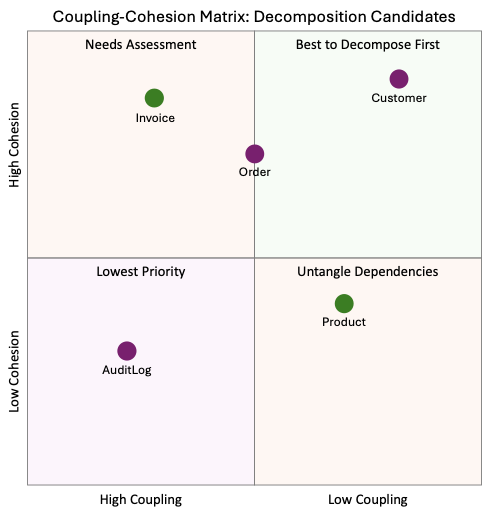 Figure 3: Coupling-cohesion matrix – showing the four quadrants and ideal candidates for decomposition
Figure 3: Coupling-cohesion matrix – showing the four quadrants and ideal candidates for decomposition
3. Migrating business logic
Database stored procedures, triggers, and functions often contain critical business logic that must move to the application layer for true service autonomy. The guide outlines a three-phase approach: analysis, classification, and migration. Modern tools accelerate this process. AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) provides initial analysis and can convert schemas to target databases.
AWS Transform for SQL Server automates stored procedure conversion from T-SQL to PL/pgSQL, maintaining business logic integrity during database modernization. Development teams can leverage Kiro CLI to streamline database operations and assist with code generation tasks during the migration process, while generative AI tools like Amazon Q Developer help accelerate application code transformation and modernization efforts, significantly reducing manual effort.
4. Decoupling table relationships
Breaking apart complex table joins and foreign key relationships is essential for independent database evolution. The APG guide describes several proven strategies:
- Denormalization intentionally duplicates data across services to eliminate cross-service lookups. While creating redundancy, it significantly improves service performance and independence.
- Reference-by-key maintains relationships through unique identifiers rather than foreign keys. Services store only IDs and retrieve additional data through API calls when needed.
- Event-based synchronization uses services like Amazon EventBridge or Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) to propagate changes. When data changes, events notify subscribed services, replacing rigid table joins with flexible, scalable patterns.
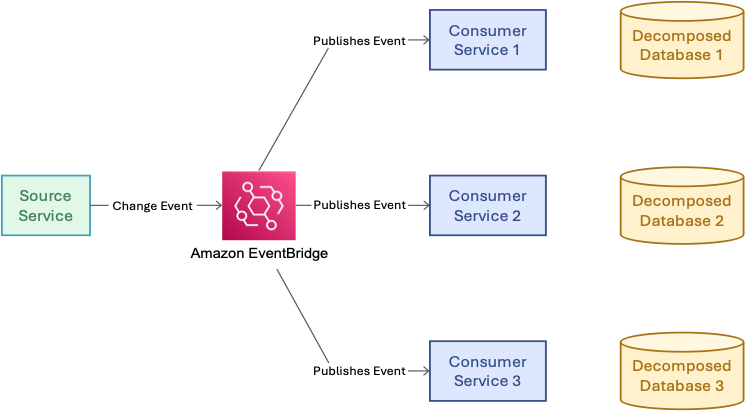 Figure 4: Event-based synchronization pattern – showing how services publish and subscribe to data change events
Figure 4: Event-based synchronization pattern – showing how services publish and subscribe to data change events
Integration with AWS migration and modernization programs
Database decomposition fits naturally within broader modernization initiatives. Organizations participating in MAP often sequence their modernization journey; migrate to AWS, containerize applications, decompose databases, and adopt cloud-native patterns. The AWS Modernization Experience-Based Acceleration (ModAx) program provides hands-on guidance for these transformations.
The approach aligns with the AWS Well-Architected Framework, particularly the Operational Excellence and Performance Efficiency pillars. Decomposed databases enable independent deployments (Operational Excellence), purpose-built database selection (Performance Efficiency), and granular cost optimization (Cost Optimization pillar).
Realizing cost savings and operational benefits
Database decomposition delivers measurable cost savings through several mechanisms:
- License optimization – Transition from expensive proprietary databases to open-source alternatives like Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition or Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL. Organizations can reduce database licensing costs by 60-90% while gaining performance improvements.
- Right-sizing opportunities – Independent databases can be sized based on actual workload rather than peak aggregate demand. A low-traffic service doesn’t need the same compute capacity as your high-traffic service, enabling precise resource allocation.
- Reduced operational overhead – Purpose-built databases often require less tuning and maintenance than monolithic databases supporting diverse workloads. Managed services like Amazon RDS and DynamoDB eliminate undifferentiated heavy lifting.
- Improved resource utilization – Independent scaling prevents over-provisioning. Services scale based on their specific demand patterns rather than being constrained by shared infrastructure limitations.
Leveraging AWS services for decomposition
AWS Transform for SQL Server accelerates full-stack database modernization through AI-powered orchestration. The service connects to SQL Server databases and .NET applications, analyzes dependencies, and creates coordinated transformation plans. AWS Transform automates schema conversion, stored procedure transformation (T-SQL to PL/pgSQL), and simultaneously refactors dependent application code—accelerating modernization by up to 5x while reducing operating costs by up to 70% through license elimination.
For data migration across all database platforms, AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) supports both full-load migrations and ongoing replication using change data capture (CDC), enabling zero-downtime transitions with synchronized source and target databases.
AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) provides automated schema conversion and detailed assessment reports for heterogeneous migrations across Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and other database platforms.
Getting started with database decomposition
Organizations beginning their database decomposition journey can follow this structured approach:
- Assess and prioritize – Conduct a comprehensive assessment of your database landscape to identify natural decomposition boundaries. Prioritize tables with high cohesion and low coupling as your first candidates—these early wins build organizational confidence and momentum.
- Engage AWS support – Work with your AWS account team to access MAP funding and technical guidance. AWS Professional Services and AWS Partners have deep experience guiding database decomposition projects.
- Implement governance – Establish oversight frameworks for data consistency, security, and compliance early in your journey. Extend monitoring and observability practices to encompass your decomposed architecture.
- Build expertise – Leverage AWS training resources through AWS Skill Builder.
Conclusion
Database decomposition unlocks the full potential of cloud-native architectures. The structured approach controlling access, analyzing dependencies, migrating logic, and decoupling relationships—provides a proven path forward refined through numerous customer engagements.
The intersection of database modernization with generative AI tools represents an exciting evolution. What once required months of manual effort can now be accelerated through AI-assisted code conversion and analysis, making database decomposition more accessible to organizations of all sizes.
Organizations participating in MAP and modernization programs are well-positioned to begin this journey. The combination of proven patterns, comprehensive tooling, AWS expertise, and potential funding creates an opportunity to transform database architectures while managing risk effectively.
Contact your AWS account team to discuss how database decomposition fits within your broader modernization strategy. Whether you’re just beginning your cloud journey or deep into transformation, decomposing monolithic databases represents a critical step toward achieving true business agility and operational excellence.