AWS Database Blog
Create a SQL Server Developer Edition instance on Amazon RDS for SQL Server
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) for SQL Server now supports SQL Server Developer Edition through the custom engine version (CEV) approach by uploading SQL Server installation files to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3). This capability enables you to use Developer Edition in development and testing environments without incurring additional licensing costs, while benefiting from the fully managed RDS infrastructure.
SQL Server Developer Edition is a full-featured edition that includes all Enterprise Edition functionality. With SQL Server Developer Edition on RDS, development teams get the Developer Edition capabilities in a managed environment with production-consistency, while paying only for AWS infrastructure—no SQL Server licensing fees. For pricing details, see Amazon RDS for SQL Server pricing.
Solution overview
Follow these three steps to create your SQL Server Developer Edition instance.
- Prepare and upload SQL Server installation files to Amazon S3, including the Developer Edition ISO and any required cumulative updates.
- Create a CEV that Amazon RDS uses to build your specific database engine configuration.
- Launch an RDS instance using the CEV, which will provide you with fully managed SQL Server Developer Edition databases.
The following figure shows the workflow described in the preceding steps.

Prerequisites
As part of the initial launch of this feature, Developer Edition is supported for SQL Server 2022 with cumulative update 21 (CU21). This feature is supported on sixth generation instance classes (M6i and R6i). For the latest list of supported instance classes, see AWS RDS SQL Server Instance Classes.
Before getting started, you must have:
- An AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) principal (role or user) that can create an RDS for SQL Server Developer Edition instance. It must have the following permissions:
- AmazonRDSFullAccess – AWS managed policy for RDS operations
- s3:GetObject – Permission to access SQL Server installation files in Amazon S3
- An S3 bucket to store installation files. All installation files must be stored in the same S3 bucket, in the same folder path, and in the same AWS region where you are creating the CEV.
Step 1: Prepare and upload installation files
To get started, download and install SQL Developer Edition and cumulative updates. As part of this step, you will create an S3 bucket to store the files.
Download SQL Server Developer Edition
- Download SQL Server 2022 Developer Edition
Note: You can also use your Visual Studio subscription to obtain Developer Edition. Download the English version, other versions are not supported. - Run the installer and choose Download Media.

- Choose English as the preferred language, select ISO as your media type and specify a download location to store the installation files. We do not support ISO files from other languages. If the ISO file isn’t English or the file doesn’t have the ISO file extension, the process of creating a Developer Edition CEV will fail.

Alternatively, after downloading the SQL Server Developer Edition installation package, you can use the following command for an unattended download of the interactive installer.
Supported cumulative updates
To view all supported engine versions for creating Developer Edition CEV, run the following AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) command:
The command returns output similar to the following:
Setting the engine version status as ‘requires_custom_engine_version’ identifies template engine versions that are supported. These templates show which SQL Server versions you can import.
Download cumulative updates
- Visit the Microsoft Update Catalog.
- Search for and download the latest RDS supported cumulative update. For this example, we’re using CU21 (SQLServer2022-KB5065865- x64.exe).
Create an S3 bucket and upload your SQL Server installation files
- The following example code creates the
amzn-s3-demo-destination-bucketbucket in theus-west-2AWS Region. - Run the following command to upload the ISO file.
- Run the following command to upload the cumulative update file.
- To check the results, go to the Amazon S3 console and browse the bucket to view its contents.

Step 2: Create a CEV
A CEV packages your SQL Server installation files into a reusable template that Amazon RDS uses to deploy instances. In this step, you create a CEV from the SQL Server installation files you uploaded to the S3 bucket.
- From the AWS Management Console for Aurora and RDS, choose Custom engine versions in the navigation pane and then choose Create custom engine version.
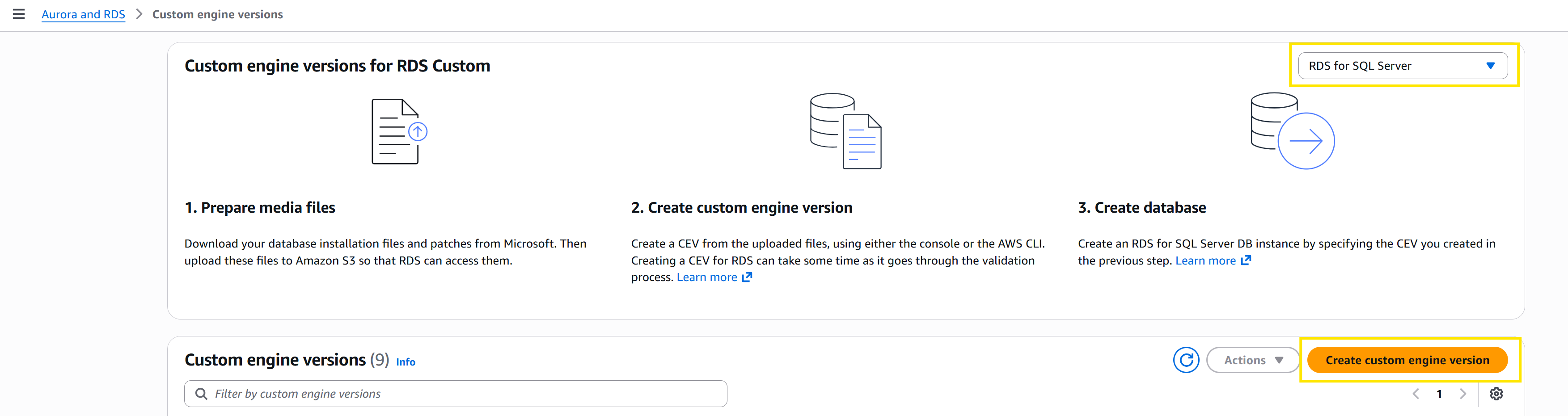
- Configure the CEV:
- Engine type: Select Microsoft SQL Server
- Edition: Select Developer Edition
- Engine version: Choose your SQL Server engine version from the dropdown menu. The menu displays supported engine versions for SQL Server Developer Edition (such as 16.00.4215.2).
- Custom engine version identifier: Enter a name, such as
sql-server-dev-edition-cev.

- Under Installation media, search for and select your ISO file and cumulative update.
- SQL installation file path:
s3://amzn-s3-demo-destination-bucket/sqlserver-dev-media/SQLServer2022-x64-ENU-Dev.iso - Cumulative update file path:
s3://amzn-s3-demo-destination-bucket/sqlserver-dev-media/SQLServer2022-KB5065865-x64.exe
- SQL installation file path:
- Choose Create custom engine version.

CEV creation typically takes 15–30 minutes. The newly created CEV will have a status of Validating until validation is complete. Monitor the CEV status in the console until it’s Available before creating RDS instances.

Alternatively, you can use the AWS CLI to create and monitor the status of a CEV.
Create a CEV
Monitor CEV creation status
Note: This command only returns CEVs with status of Available. To view CEVs in Validating or other states, include the --include-all flag.
Step 3: Launch an RDS instance
After your CEV shows Available status, you can create RDS instances that use your custom SQL Server Developer Edition configuration. The instances will be deployed with your specific SQL Server version and cumulative updates.
- From the AWS Management Console for Aurora and RDS, choose Databases in the left navigation pane, then choose Create Database.
- In the Create database page, provide the desired settings for your instance, making sure your Engine options are set correctly.
- Engine type: Select Microsoft SQL Server
- Database management type: Select Amazon RDS
- Edition: Select SQL Server Developer Edition
- Custom engine version: Select your desired CEV from the dropdown menu

- Define your settings for DB instance size, Storage, Connectivity to fit your use case.
- Choose Create database.
Alternatively, you can use the AWS CLI to create an RDS instance.
Important limitations and considerations
SQL Server Developer Edition on Amazon RDS has the following limitations and considerations:
- You are responsible for ensuring that your usage complies with Microsoft’s licensing terms and that production workloads use appropriately licensed SQL Server editions.
- Multi-AZ deployments and read replicas are not currently supported.
- CEVs are Region and account specific and can’t be copied across Regions or shared across AWS accounts. See the Amazon RDS Documentation for current Regional availability.
- To upgrade your DB instance with the latest cumulative update, you’ll need to create a new CEV using the most recent CU supported by Amazon RDS. You’ll need to follow the same process of creating a new CEV as described in this post to apply the latest updates to your database instances. For more information, see Applying database minor version upgrades.
- You cannot delete a CEV if there are any associated resources, including RDS DB instances, DB snapshots, or backups.
- While SQL Server Developer Edition itself is free for development and testing purposes, you still need to consider the following costs:
- Amazon RDS instance costs
- Amazon RDS Storage costs for your database and backups
- Amazon S3 storage costs for installation files
- Data transfer costs
- Keep your installation files and cumulative updates current to maintain security and performance.
- Combine the use of Developer Edition to maximize cost savings for your lower environments and implement scheduled shutdowns when they’re not needed.
Clean up
To prevent ongoing charges, clean up the resources that you created in this walkthrough when you no longer need them.
- Delete your RDS for SQL Server instance. For instructions, see Deleting a DB instance.
- Delete the Custom engine Version. For instructions, see Deleting Custom engine versions.
- Delete the S3 bucket. For instructions, see Delete Bucket.
Conclusion
In this post, we showed you how to create and deploy SQL Server Developer Edition on Amazon RDS. You saw the complete process from preparing your installation files and uploading them to Amazon S3, to creating a CEV, and finally launching your RDS instance.SQL Server Developer Edition on Amazon RDS provides Enterprise Edition capabilities and Amazon RDS-automated management features in non-production environments without Enterprise licensing fees. You can create CEVs from installation files uploaded to Amazon S3 and use them to create multiple database instances for development and test environments while ensuring production level consistency.