AWS Database Blog
Category: Amazon Aurora
Use default encryption at rest for new Amazon Aurora clusters
In this post, you learn how Amazon Aurora now provides encryption at rest by default for all new database clusters using AWS owned keys. You’ll see how to verify encryption status using the new StorageEncryptionType field, understand the impact on new and existing clusters, and explore migration options for unencrypted databases.
Achieve near-zero downtime database maintenance by using blue/green deployments with AWS JDBC Driver
In this post we introduce the blue/green deployment plugin for the AWS JDBC Driver, a built-in plugin that automatically handles connection routing, traffic management, and switchover detection during blue/green deployment switchovers. We show you how to configure and use the plugin to minimize downtime during database maintenance operations during blue/green deployment switchovers.
Migrate relational-style data from NoSQL to Amazon Aurora DSQL
In this post, we demonstrate how to efficiently migrate relational-style data from NoSQL to Aurora DSQL, using Kiro CLI as our generative AI tool to optimize schema design and streamline the migration process.
Build a custom solution to migrate SQL Server HierarchyID to PostgreSQL LTREE with AWS DMS
In this post, we discuss configuring AWS DMS tasks to migrate HierarchyID columns from SQL Server to Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible efficiently.
Auto Analyze in Aurora DSQL: Managed optimizer statistics in a multi-Region database
In this post, we give insights into Aurora DSQL Auto Analyze, a probabilistic and de-facto stateless method to automatically compute DSQL optimizer statistics. Users who are familiar with PostgreSQL will appreciate the similarity to autovacuum analyze.
Strategies for upgrading Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL and Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL from version 13
In this post, we help you plan your upgrade from PostgreSQL version 13 before standard support ends on February 28, 2026. We discuss the key benefits of upgrading, breaking changes to consider, and multiple upgrade strategies to choose from.
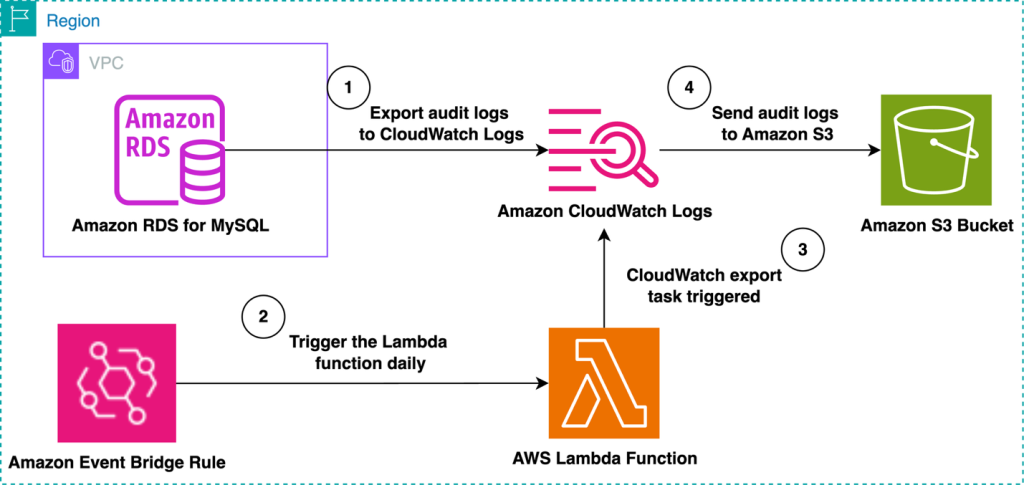
Automate the export of Amazon RDS for MySQL or Amazon Aurora MySQL audit logs to Amazon S3 with batching or near real-time processing
Amazon RDS for MySQL and Amazon Aurora MySQL provide built-in audit logging capabilities, but customers might need to export and store these logs for long-term retention and analysis. Amazon S3 offers an ideal destination, providing durability, cost-effectiveness, and integration with various analytics tools. In this post, we explore two approaches for exporting MySQL audit logs to Amazon S3: either using batching with a native export to Amazon S3 or processing logs in real time with Amazon Data Firehose.
Using the shared plan cache for Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL
In this post, we discuss how the Shared Plan Cache feature of the Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition can significantly reduce memory consumption of generic SQL plans in high-concurrency environments.
AWS Organizations now supports upgrade rollout policy for Amazon Aurora and Amazon RDS automatic minor version upgrades
AWS Organizations now supports an upgrade rollout policy, a new capability that provides a streamlined solution for managing automatic minor version upgrades across your database fleet. This feature supports Amazon Aurora MySQL-Compatible Edition and Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition and Amazon RDS database engines MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, SQL Server, Oracle, and Db2. It eliminates the operational overhead of coordinating upgrades across hundreds of resources and accounts while validating changes in less critical environments before reaching production. In this post, we explore how upgrade rollout policy works, its key benefits, and how you can use it to implement a systematic approach to database maintenance across your organization.
Unlock Amazon Aurora’s Advanced Features with Standard JDBC Driver using AWS Advanced JDBC Wrapper
In this post, we show how you can enhance your Java application with the cloud-based capabilities of Amazon Aurora by using the JDBC Wrapper. Simple code changes shared in this post can transform a standard JDBC application to use fast failover, read/write splitting, IAM authentication, AWS Secrets Manager integration, and federated authentication.