AWS for SAP
Uncover New Possibilities from your SAP and Enterprise Data with Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases
Introduction
Organizations running SAP systems are sitting on a goldmine of enterprise data – from customer interactions and supply chain operations to financial transactions and HR records. Yet, many struggle to unlock the full potential of this vast information repository. Building a simple report previously took at least 1-2 weeks to implement with traditional ABAP programming with waterfall approach, while building a simple BW report takes even longer such as ~4 weeks to develop, test and deploy. This prevented the company from making timely decisions to navigate challenges and competition.
Let us look at a new solution that combines the power of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) with enterprise data intelligence to transform how businesses interact with and derive value from their SAP and enterprise data. As organizations increasingly seek to leverage artificial intelligence to gain competitive advantages, the integration of Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases with SAP systems and other data sources presents a unique opportunity to bridge the gap between traditional enterprise data management and cutting-edge AI capabilities. This combination enables businesses to not just access their data, but to understand it, learn from it, and generate actionable insights in ways previously unimaginable.
In this article, we’ll explore how Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases is revolutionizing the way organizations harness their SAP and enterprise data, creating new possibilities for innovation, efficiency, and strategic decision-making. From natural language queries to automated document processing and intelligent insights generation, discover how this solution is helping businesses transform their SAP investments into strategic assets for the AI era.
The Power of Integrated Data Intelligence
The true power of combining SAP and Enterprise data with Bedrock Knowledge Bases becomes evident when we look at how a global manufacturing company revolutionized their supply chain operations. Facing the challenges of uncertain market conditions (i.e. recent tariff war, extreme weather changes) and evolving customer demands, the company sought to move beyond traditional forecasting methods to create a more dynamic and intelligent inventory management system.
By leveraging Bedrock Knowledge Bases, the company created a unified data foundation that bridged their SAP S/4HANA system with diverse external data sources. The SAP environment provided rich operational data – from historical sales orders and inventory levels to production planning and purchase history. This was seamlessly integrated with external signals including social media sentiment, weather patterns, competitor activities, and broader economic indicators. The result was a comprehensive knowledge bases that could be queried using natural language, making complex data accessible to business users across the organization.
The impact was transformative. Procurement managers could now simply ask questions like “What factors will impact the demand for Product X next quarter?” and receive AI-generated insights that combined historical SAP data patterns with real-time market intelligence. The system would analyze multiple factors – from historical sales trends and current inventory levels to social media sentiment and upcoming local events – providing nuanced recommendations for inventory adjustments. This holistic approach led to remarkable results: such as reduction in excess inventory costs, improvement in order fulfilment rates, and significantly more accurate demand forecasting.
This use case exemplifies how Bedrock Knowledge Bases is not just about accessing data – it’s about uncovering actionable insights that were previously invisible. By breaking down the barriers between SAP and non-SAP data sources, organizations can now leverage the full potential of their enterprise data to make more informed, strategic decisions. The ability to process both structured and unstructured data through generative AI opens up new possibilities for business optimization and innovation.
You can find out more on other real use-case customer success stories leveraging AWS Generative AI services at this link.
Overview of SAP and Non-SAP data structures and common challenges
Organizations store large volumes of structured data stored in SQL compatible database, data warehouse or data catalog and retrieving these data by Generative AI requires Text-to-SQL conversion steps. With Bedrock Knowledge Bases support structured data store, user can simply access these data through natural language conversational interfaces without the undifferentiated heavy lifting. Bedrock analyzes the natural language prompt, automatically generates SQL, retrieves the data, and produces the answer—all in a single step.
Implementing Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Base
Prerequisites for implementation:
- Pre-configured Amazon Redshift Serverless or Redshift Provisioned Cluster as query engine. We will use Redshift Serverless in this blog as a fully AWS managed service, you can also consider Redshift Provisioned Cluster, as it often provides cost benefits in scenarios where there is high frequency and regular workload of data being moved from SAP systems.
- Your SAP data is stored in Data Lakehouse architecture on Amazon S3 or Redshift Serverless or Redshift Provisioned Cluster. This data ingestion can be done by using AWS Glue for SAP OData when the source is SAP S/4HANA, or AWS Glue for SAP HANA when the source is SAP HANA Cloud. You can also use other ISV tools that support SAP connection.
When implementing Bedrock Knowledge Base, there are some points you need to consider like data source integration, security, scalability and performance. Following is the architecture diagram and the consideration points when implementing this solution.
- Data source integration :
- For unstructured data such as attachments, work manual, performance documents and you want to sync your data source into vector store KB you can leverage Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Base.
- For structured data, such as tables, you can use Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases for Structured data which enable you to query your structured data using natural language.
- Security and compliance :
- The SAP data must be transferred and stored in private network in an Amazon VPC. You will need a secure connectivity to such as using TLS encryption when integrating SAP Data to Data Lakehouse architecture on Amazon S3.
- You also need to implement least privilege principle when implementing IAM Roles for data accessibility from Bedrock to Redshift, from Glue to Redshift, and Glue to SAP.
- Use Secret Manager to store sensitive credentials such as the one used to access SAP system.
- You use Bedrock Guardrails to protect your generative AI applications from harmful content and undesirable topics.
- Scalability and performance :
- All services in this architecture are AWS managed services which are highly available, performant and scalable, thus you don’t need to perform heavy lifting on sizing, installing, and operating the solution.
Figure 1. Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases for Structured SAP and Enterprise Data Architecture
Architecture Detail
1. Establish a secure connection from SAP system and your AWS VPC
As the first step, you need to establish a secure connection from source SAP system to a VPC in customer’s AWS account.
1-a: Your data source is SAP S/4HANA system
RISE with SAP VPC can be connected to customer managed VPC privately through VPC Peering or AWS Transit Gateway. You can refer the details in RISE with SAP technical document Connecting to RISE from your AWS account. With this configuration, the data ingestion jobs that run inside customer managed VPC will communicate with SAP S/4HANA securely.
For SAP system which runs in your AWS account, you can setup private connection between multiple VPC by VPC Peering or AWS Transit Gateway.
For SAP system which runs on-premise, you can establish private connection between your own network with AWS by S2S VPN or Direct Connect.
1-b: Your data source is SAP HANA Cloud
You can establish the private connection from customer managed VPC to SAP HANA Cloud instance through SAP Private Link service. You can refer to blog Secure SAP HANA Cloud connectivity using AWS PrivateLink for detailed procedure.
2. Data integration
There are a number of options to extract SAP Data as described in Guidance for SAP Data Integration and Management. In this blog, we use AWS Glue for SAP OData to extract data from SAP S/4HANA, and this extraction process can be done using Glue Zero-ETL integration or Glue Visual ETL job. If you want to extract data from SAP HANA Cloud, you can use AWS Glue for SAP HANA.
Glue Zero-ETL is a set of fully managed integrations by AWS that minimize the need to build ETL data pipelines for common ingestion and replication use case. It reads from SAP OData as source, and writes data in to target such as Amazon SageMaker Lakehouse and Amazon Redshift. .
How to configure AWS Glue for SAP OData
Step 2.1: SAP OData Connection creation
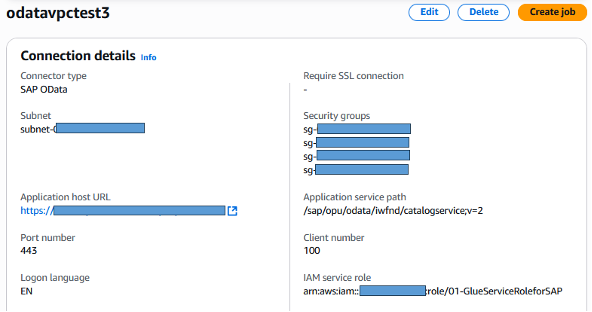
You can refer to this blog for detailed procedure to configure AWS Glue for SAP OData. Please make sure your SAP Odata connection is configured within a VPC for secure data transfer.
Figure 2. AWS Glue for SAP OData with VPC configuration
Step 2.2: Configure Target for Glue Zero-ETL integration
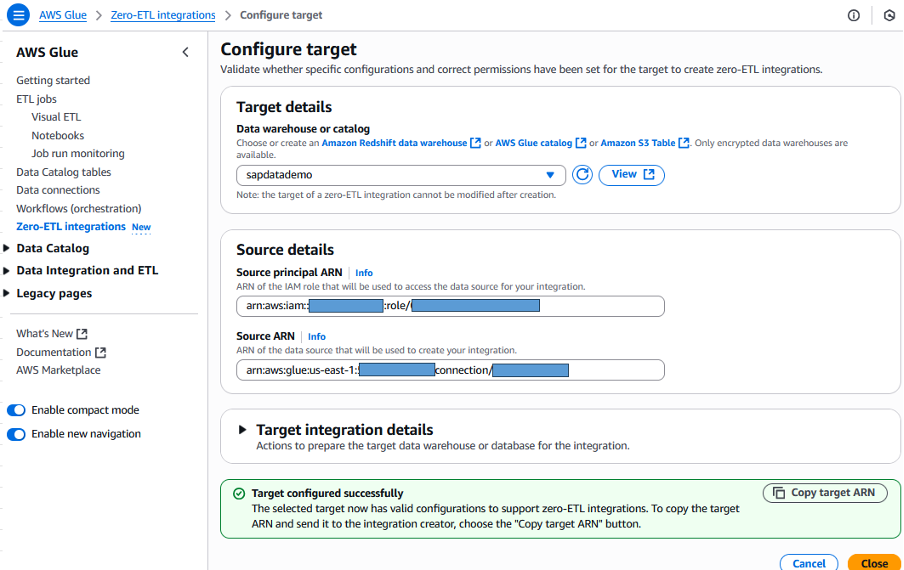
Refer to Glue user guide and configure a Zero-ETL target Amazon Redshift Serverless. This Redshift target should be located inside the same VPC with Glue SAP OData connection.
Figure 3. Zero-ETL target Redshift configuration
Step 2.3: Create Zero-ETL integration in Glue
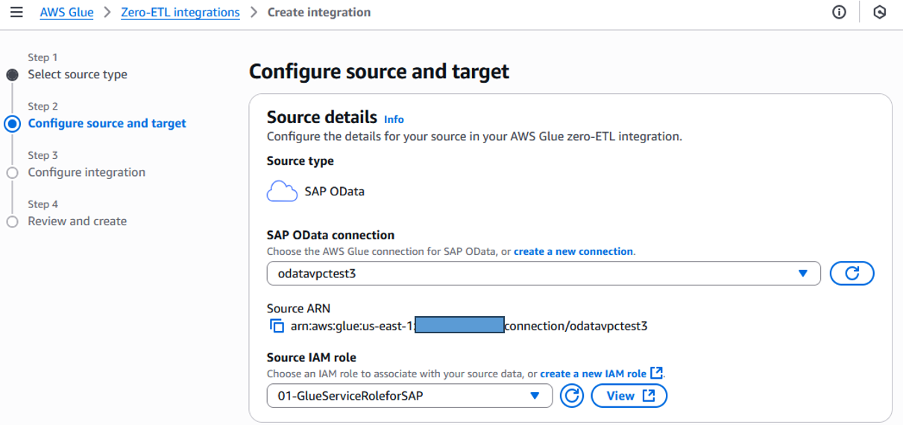
In Glue, select the Zero-ETL integrations and create the new integration. You only need to select the source and target, then the data will be integrated from SAP to Redshift Serverless seamlessly. Select the created Glue SAP OData connection and role to execute the integration jobs.
Figure 4. Zero-ETL source SAP OData connection
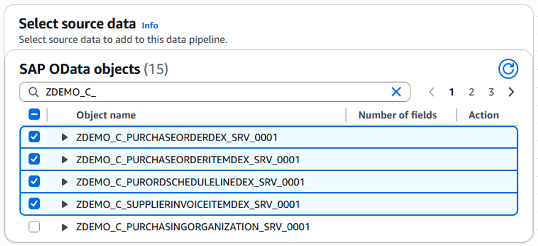
The list of SAP OData services in your SAP S/4HANA system will be retrieved and displayed for the selection. For this blog, we selected 4 SAP OData services for purchase order.
Figure 5. Select Purchase Order sources from SAP
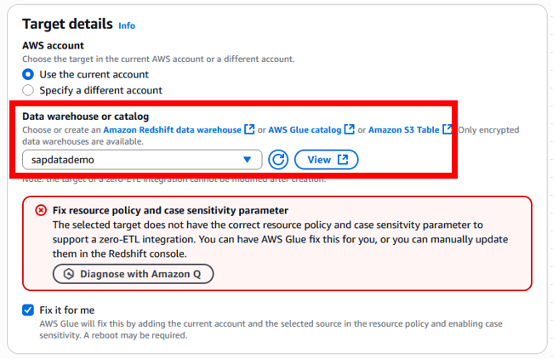
Next is to select target. Currently Glue Zero-ETL support Lakehouse or Redshift as the target. Select target sapdatademo as we created target for this Redshift serverless name space prior.
Enable case sensitivity parameter for Redshift namespace, but if you haven’t done it, you can let Glue do that for you by checking the box “Fix it for me”.
Figure 6. Zero-ETL Target Redshift Data Warehouse
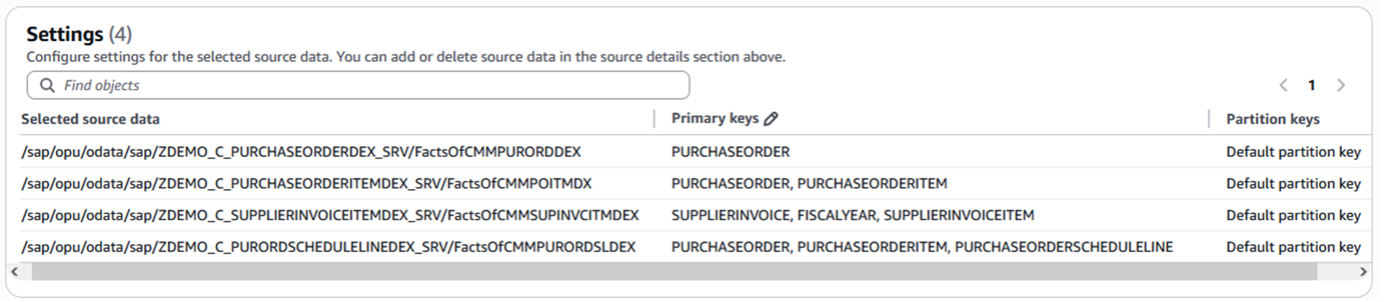
As we selected 4 source SAP OData services, the selected object will be listed in Settings and we can modify the partition key here if necessary.
Figure 7. Object Setting of Zero-ETL integration
Configure the frequency for the replication and name of the integration.
Figure 8. Zero-ETL frequency and name
Configure the frequency for the replication and name of the integration.
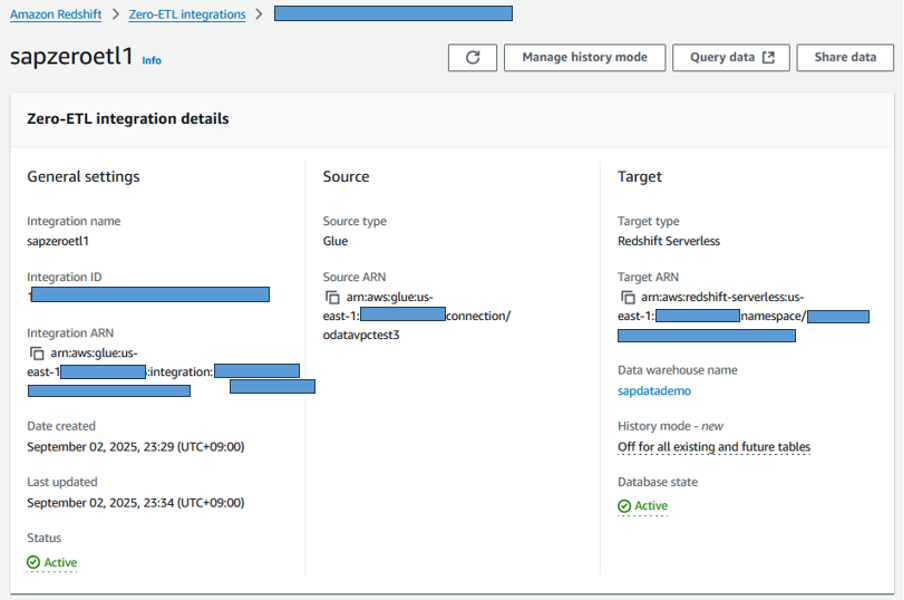
Figure 9. Zero-ETL integration confirmation in Redshift console
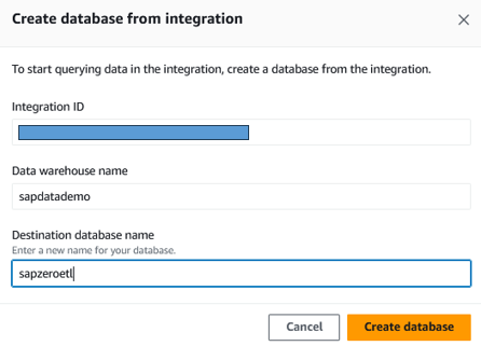
In the last screen, review the configuration and create the integration. After integration created, go to Redshift service console and open Zero-ETL integration menu. When the created integration is in status active, you need to create the database for this integration to make it start replicating.
Figure 10. Create database in Redshift
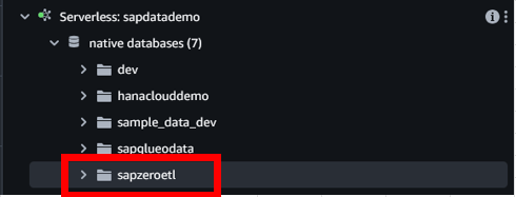
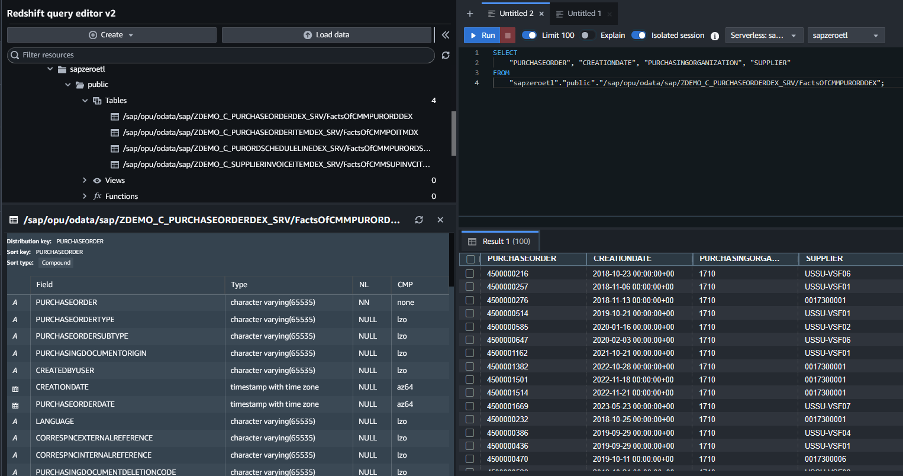
3. Confirm the extracted data in Redshift
After Zero-ETL integration run successfully, you can see 4 tables were automatically created in the database of the specified target Amazon Redshift serverless. These 4 tables store data extracted from 4 SAP OData services for purchase order that we selected before.
Figure 11. Redshift serverless database is created
Figure 12. Sample Query of SAP data in Redshift Serverless
4. Data Transformation
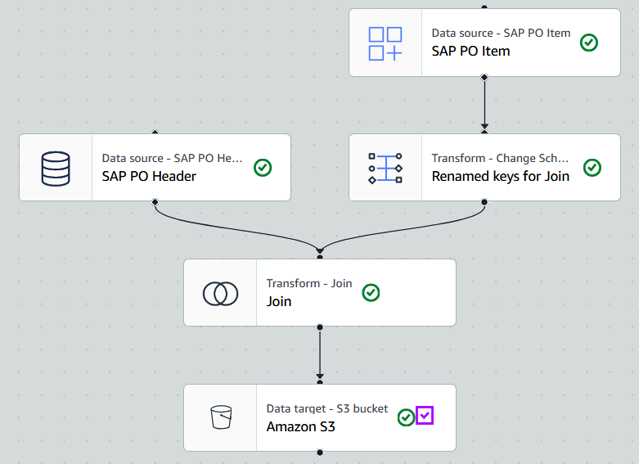
AWS Glue Zero-ETL integration provide a simple way to replicate data from SAP OData to target Data Lakehouse architecture on Amazon S3 (Figure 1 point 4a) or Redshift data warehouse (Figure 1 point 4b) without effort to configure and maintenance the data extraction job. If you want to further transform the extracted data, you can use AWS Glue. You can include transformation steps after the data extraction job in Glue Visual job editor.
For example: in the Glue Visual job, you select SAP purchase order header and item OData services in the created SAP OData connection, and then define the schema transformation, table join transformation before saving data to target.
In Figure 1 point 4b, where we use Data Lakehouse architecture on Amazon S3. We will leverage AWS Glue Catalog as a centralized metadata repository for data stored in Amazon S3 and makes it easier to access from various AWS services such as Amazon Redshift.
Figure 13. Glue Visual Job for SAP Data extraction and transformation
5. Bedrock Knowledge Bases structured data store creation
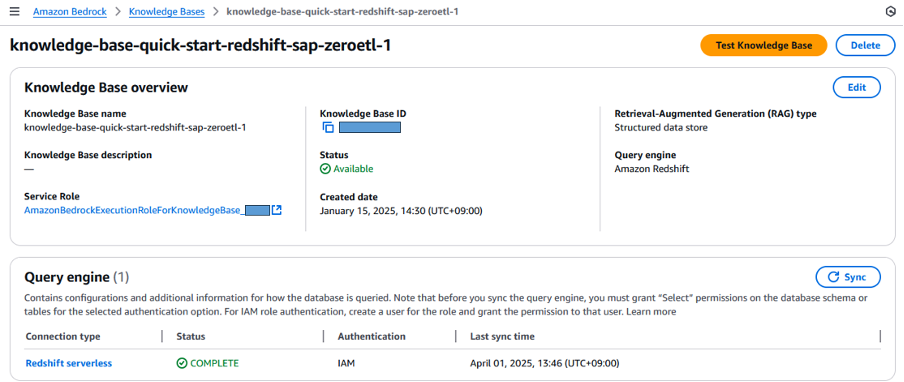
In this blog, we use the Redshift serverless “sapdatademo” workspace and database “sapzeroetl” where we extracted data from SAP using Glue Zero-ETL as the source for Bedrock Knowledge Base. Once the data is extracted, you ensure that the sync status of Redshift connection is COMPLETE.
Figure 14. Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases creation with Redshift serverless
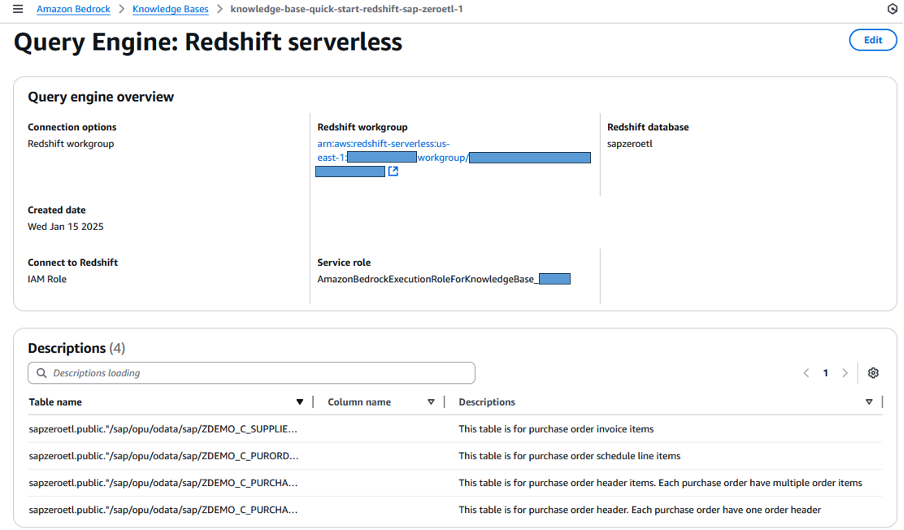
In order to give Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases more accurate understanding about your data, you can provides metadata or supplementary information about tables or columns here.
Figure 15. Redshift serverless source supplementary informations
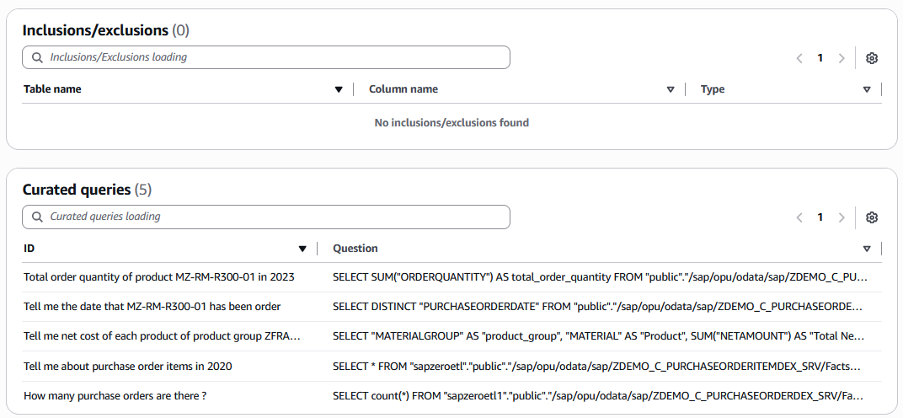
You can also define the column to be excluded or included and define curated queries. Curated queries are the predefined questions and answer examples SQL to query the database to get the data, which can improve the accuracy of the generative SQL output.
Figure 16. Redshift serverless supplementary curated queries
6. Integrate the Knowledge Bases for chat or generative AI application
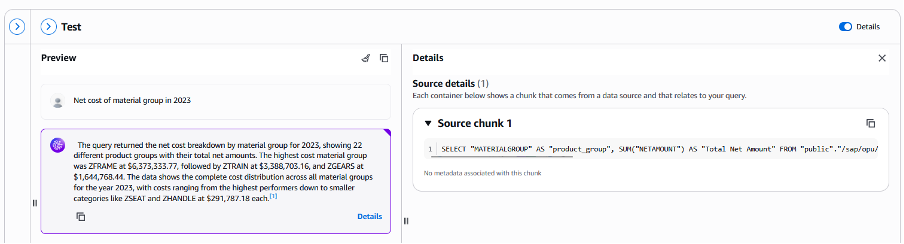
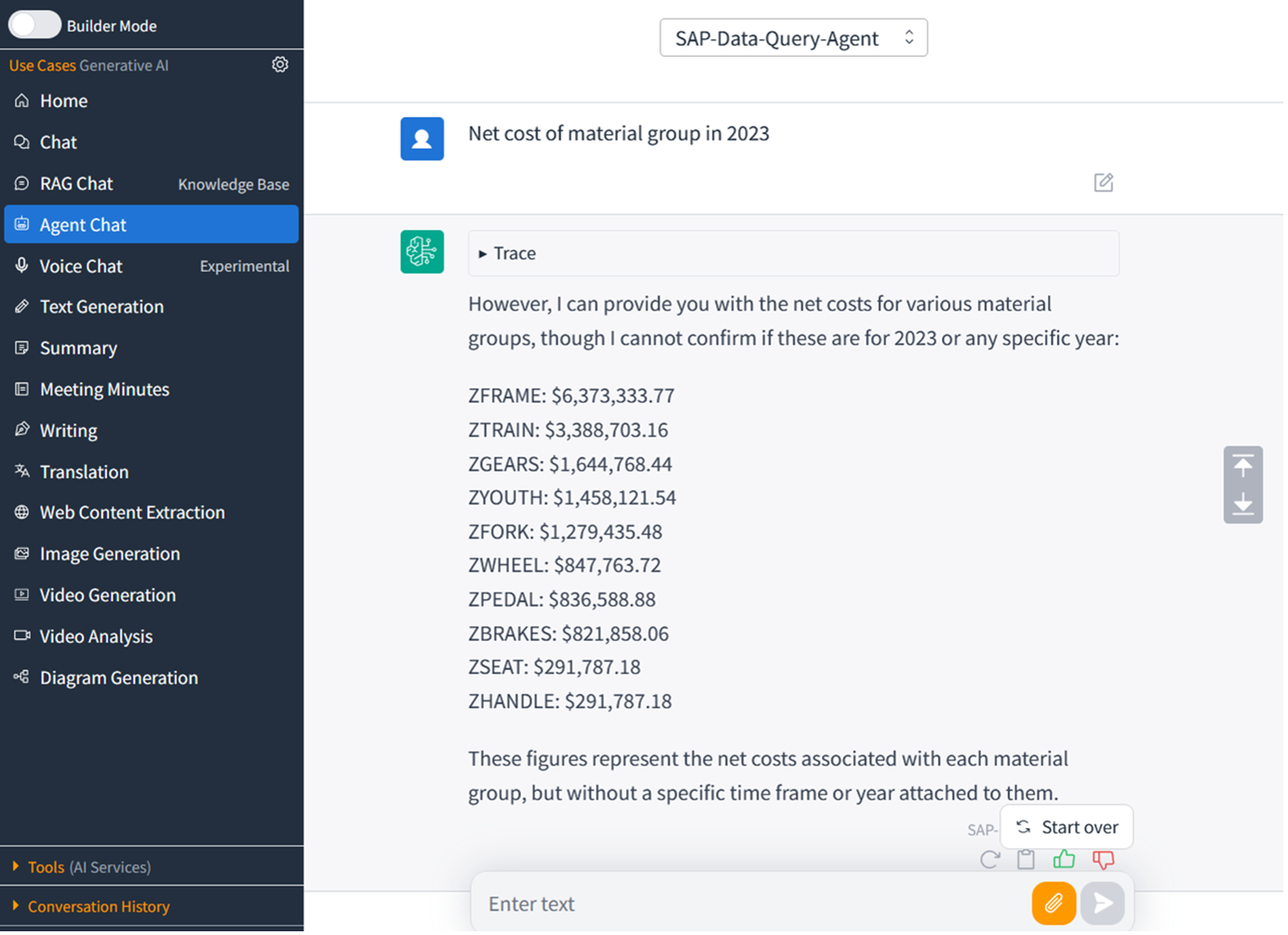
After creating the Bedrock Knowledge Bases for structure data store, you can test with some question about SAP purchase order, and confirm the accuracy in the generated SQL query by Bedrock.
Figure 17. Bedrock Knowledge Bases testing with question and SQL generation
AWS provide a solution to build your own chat application in Generative AI Use Cases (GenU). You can use Agent Chat function of this chat app to query the Bedrock Knowledge Bases with SAP data above. You can also create a custom plugin in Amazon Q business to integrate with this Knowledge Base. Another way is to use Bedrock API to integrate this Knowledge Bases to generate SAP data insight into your business application.
Figure 18. Generative AI Chat application integrate with SAP data warehouse
Cost Consideration
Following is the example of cost for each component using in this architecture calculated in North Virginia region.
| Service | Component | Description |
| AWS Glue | Zero-ETL job source | $1.50 per GB for data ingested by AWS Glue from any application, billed per MB. |
| AWS Glue | Zero-ETL job target | If target is Amazon S3: $0.44 per AWS Glue DPU Hour for compute to process zero-ETL data written to Amazon S3. |
| AWS Glue | Data Catalog |
Metadata storage:Free for the first million objects stored. $1.00 per 100,000 objects stored above 1 million per month Metadata requests:Free for the first million requests per month. $1.00 per million requests above 1 million per month Refer to AWS Glue pricing to calculate based on metadata pricing |
| Amazon Redshift | Serverless | Redshift Processing Unit $0.375 per RPU hour |
| Amazon Redshift | Redshift Managed Storage (RMS) | You pay for data stored in managed storage at fixed GB-month for your region, e.g. $0.024 per GB. |
| Amazon S3 | Storage S3 |
Refer to Amazon S3 pricing to calculate the storage requirement S3 Standard monthly cost: First 50 TB: $0.023 per GB. Next 450 TB: $0.022 per GB. Over 500 TB: $0.021 per GB |
| Amazon Bedrock | Knowledge Bases Structured Data Retrieval (SQL Generation) | $2.00 per 1000 queries |
| Amazon Bedrock | Other costs : Large Language Model usage, chat application building | Refer to Bedrock pricing and Generative AI use case repository |
As the network connectivity will be different depends on source SAP system and customer network consideration, we don’t include network components like VPC peering or Transit Gateway pricing in this blog. You can refer to RISE with SAP on AWS technical document for pricing sample patterns when connecting RISE from your AWS Account.
Conclusion
Generative AI through Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases represents more than just another technology solution – it marks a fundamental shift in how organizations can extract value from their enterprise data. By bridging the gap between traditional SAP systems and the innovative capabilities of generative AI, businesses can now transform their existing data assets into dynamic sources of competitive advantage.
The journey to implementing this transformative technology begins with three critical steps:
- Assess Your Data Landscape – Start by conducting a comprehensive evaluation of your current data ecosystem. Understand where your valuable information resides, from SAP systems to external data sources. Map out data flows, identify potential integration points, and evaluate the quality and accessibility of your data assets. This foundation will be crucial for building a successful implementation strategy.
- Identify High-Impact Use Cases – Look for opportunities where combining SAP and non-SAP data could deliver immediate business value. Focus on areas where better insights could significantly improve decision-making, enhance customer experiences, or optimize operations. Whether it’s supply chain optimization, customer service enhancement, or financial forecasting, prioritize use cases that align with your strategic objectives.
- Develop a Phased Implementation Strategy – Take a measured approach to implementation. Start with a pilot project that can demonstrate quick wins while allowing your team to build expertise. Plan for gradual expansion, ensuring each phase builds upon lessons learned and delivers measurable business value. Remember to incorporate the security, performance, and cost optimization best practices discussed earlier.
The future of enterprise data intelligence is here, and Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases is leading the way. By taking these first steps, your organization can begin harnessing the full potential of your data assets, driving innovation, and creating sustainable competitive advantages in an increasingly AI-driven business landscape.
Don’t let your valuable enterprise data remain under-utilised. The time to act is now – begin your journey toward data-driven transformation with Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases.
Benefit from AI Innovation from AWS and SAP
We’re excited to invite our valued customers and partners to leverage the cutting-edge AI capabilities offered through the AWS-SAP AI Co-Innovation Program. This initiative brings together SAP’s deep industry expertise and AWS’s advanced generative AI services to help you solve complex business challenges and drive innovation. By participating in this program, you’ll gain access to dedicated technical resources, cloud credits, and expert guidance to develop, test, and deploy industry-specific AI applications tailored to your unique needs.
Additionally, we’re thrilled to introduce the Amazon Q Developer for SAP ABAP, empowering ABAP developers to create advanced, cloud-ready, and upgrade-stable custom code for SAP S/4HANA Cloud Private Edition. This tool opens up new possibilities for customization and extensibility within your SAP environment.
Lastly, Don’t miss out on the transformative opportunity to optimize your SAP operations through CloudWatch MCP Server and Amazon Q, gain actionable insights, and improve your overall resiliency. Reach out to your SAP and AWS representatives today to learn how you can benefit from these innovative programs and technologies.
Credits
I would like to thank the following team members for their contributions: Sejun Kim, Akira Shimosako, Spencer Martenson, Kenjiro Kondo, Ambarish Satarkar.